▼ Microsoft gets real time AI via cloud! [08-28-17]
 In a bid to make artificial intelligence more accessible all-round, Microsoft has kicked off a new project which delivers real-time AI via the cloud. In a bid to make artificial intelligence more accessible all-round, Microsoft has kicked off a new project which delivers real-time AI via the cloud.
It is utilizing some nifty technology from Intel.
Project Brainwave is described by Microsoft as a deep learning acceleration platform which employs Intel’s Stratix 10 FPGA (field programmable gate array) hardware accelerator to run AI.
This is through the cloud and still deliver near-instant results.
The system is capable of processing and transmitting data with ‘ultra-low latency’, delivering results as fast as that data comes in, and so effectively operating in real-time.
And that’s a clear boon for the sort of applications that need this, from digital assistants through to the likes of autonomous driving.
The system has already shown that Intel’s Stratix 10 tech can exceed 39 Teraflops in terms of performance on a single request.
Microsoft engineer Doug Burger notes that at that level of performance, the Brainwave architecture sustains execution of over 130,000 compute operations per cycle.
It is driven by one macro-instruction being issued each 10 cycles.
Running on Stratix 10, Project Brainwave thus achieves unprecedented levels of demonstrated real-time AI performance on extremely challenging models.
And further gains are expected as Microsoft hones the system over the next year or so.
Project Brainwave supports deep learning frameworks including Microsoft’s own Cognitive Toolkit and Google’s Tensorflow, and the firm is planning to bring it to Azure customers as well.
Powerful real-time AI processing capabilities on tap will be another major string to Azure’s bow.
|
▼ Scientists discover biomarker for tongue cancer [08-24-17]
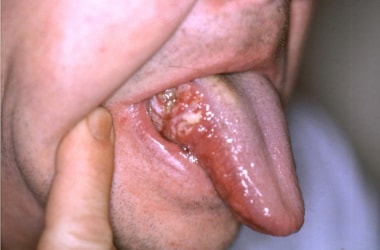 Researchers at the Tata Memorial Centre in Mumbai have identified a biomarker that will help doctors decide whether patients with early-stage tongue cancer should undergo neck surgery to remove 20-30 lymph nodes. Researchers at the Tata Memorial Centre in Mumbai have identified a biomarker that will help doctors decide whether patients with early-stage tongue cancer should undergo neck surgery to remove 20-30 lymph nodes.
Patients negative for the biomarker can be spared of neck dissection.
Studies were carried out on 57 patients.
In nearly 70% of patients with early-stage tongue cancer, the tumour does not spread to the lymph nodes.
But in the absence of a reliable biomarker capable of pointing out in which patients the disease will recur, doctors routinely remove the affected part of the tongue and the lymph nodes in all patients.
Nearly 80% of patients survive and are disease-free if tongue cancer is detected early.
But once cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, the survival rate reduces to 40%.
Currently, surgical removal of lymph nodes and studying them is the only way of knowing if the cancer has spread.
The discovery of the biomarker — MMP10 protein — potentially fills this gap.
Only those patients who have higher level of this protein [overexpression] are likely to have cancer spread to the lymph nodes.
So the biomarker will help doctors to decide which patients could be spared of complex surgeries to remove the lymph nodes.
The biomarker can be identified using a simple immuno histochemical analysis, a method to locate proteins in tissue sections.
The researchers validated their findings using data of 253 patients from the Cancer Genome Atlas and other studies.
The MMP10 biomarker was significantly higher in four of the five data sets.
The 57 patients studied were negative for human papillomavirus (HPV) but were habitual users of chewing tobacco.
Although chewing tobacco has been associated with oral cancer, there has been no direct evidence linking the two at the genome level.
This study has for the first time shown a direct link between chewing tobacco and tongue cancer.
Those chewing tobacco had a classic signature in the genome in the form of a specific type of mutation (transversion mutation).
According to the study, 53% of all patients have this tobacco signature.
This mutation is driven by tobacco usage.
|
▼ Scientists create original music from eclipse [08-23-17]
 Scientists, including one of Indian origin, have created an original music composition. Scientists, including one of Indian origin, have created an original music composition.
This is using data from the movements of the Sun, the Moon and the gradual darkness during the total solar eclipse in the U.S.
This is the first time researchers have made music with eclipse information.
The team from Georgia Institute of Technology in the U.S. watched countless videos of total eclipses to develop the correct tone and pacing for the piece.
They also used live data from the total solar eclipse, that swept across the U.S. on August 21, to add more musical elements to the existing piece.
The researchers, including Avrosh Kumar, talked to two blind people. One had previously seen an eclipse.
The other described how she listens to her surroundings, allowing researchers to better understand how visually impaired people use ambient sounds to develop a sense of their environment and the moments in their lives.
The audio experience at times sounds both hopeful and ominous.
During first contact, as the Moon starts to slide in front of the sun, high tonal sounds - representing the moon - gradually increase in volume and consistency.
During second contact, or the beginning of totality, the musical tension continues to rise.
This is even as the overall pitch and loudness begin to diminish as light levels fade.
In this portion of the music, the sound of crickets is also heard to signify the “false dusk” effect created when the moon completely covers the sun.
|
▼ Meet Versius, the world’s smallest surgical robot [08-22-17]
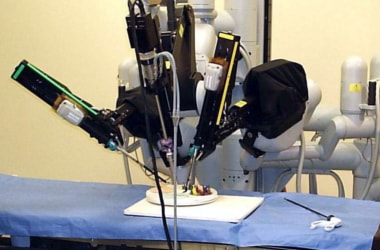 Scientists in the UK have developed the world’s smallest surgical robot with low-cost technology used in mobile phones and space industries. Scientists in the UK have developed the world’s smallest surgical robot with low-cost technology used in mobile phones and space industries.
The robot, called Versius, mimics the human arm and can be used to carry out a wide range of procedures.
It is in these that a series of small incisions are made to circumvent the need for traditional open surgery.
These include hernia repairs, colorectal operations, as well as prostate, ear, nose and throat surgery.
Such procedures reduce complications and pain after surgery and speed up recovery time for patients.
The robot is controlled by a surgeon at a console guided by a 3D screen in the operating theatre.
The robot is much easier to use than existing systems, and take up about a third of the space of current machines.
For robots to revolutionise surgery, they need to be versatile, easy to use and small.
This is so that surgical staff can move them around the operating room or between operating theatres, or pack them away when they are not being used.
This is the first robotic arm to be designed specifically for laparoscopic surgery which does that.
One of the key benefits of the robot is that it works like a human arm and contains technology that detects resistance to make sure the right amount of force is used when the instruments are inside the patient.
Researchers used electronics from mobile phones to help the robot “think” and process information, and gear box technology.
This is originally designed for the space industry to help it move.
The robot is set to be launched next year.
|
▼ China launches its first cyber-court in e-commerce hub Guangzhou [08-22-17]
 China today launched its first cyber court specialising in handling internet-related cases in the e-commerce hub of Hangzhou. China today launched its first cyber court specialising in handling internet-related cases in the e-commerce hub of Hangzhou.
This is amid a spike in the number of online disputes.
The Hangzhou Internet Court in Hangzhou, capital of east China’s Zhejiang Province will handle cases such as online trade disputes and copyright lawsuits.
The cases handled by the court will be tried online.
Yesterday, the Hangzhou municipal legislature appointed the president, vice presidents and judges of the court.
Hangzhou is home to many Internet companies, including e-commerce giant Alibaba.
The latest report from the China Internet Network Information Centre showed that China had about 751 million netizens and 724 million mobile Internet users as of the end of June.
|
▼ Now a strong glue for foetus surgery inspired by mussels [08-22-17]
 Inspired by the animal world, scientists have developed a strong glue that could make performing surgery on foetuses safer. Inspired by the animal world, scientists have developed a strong glue that could make performing surgery on foetuses safer.
Researchers made by the glue after studying how mussels maintained a tenacious grip on slippery rocks.
An adhesive that can prevent the amniotic sac from tearing after surgery could help the foetus remain in the womb longer.
This would potentially lead to a healthier future for the baby.
Scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, infused the mussel adhesive in a special polymer to make the glue.
|
▼ Artificial womb to help premature babies [08-21-17]
 Scientists have developed an artificial womb that has been successfully used to incubate healthy baby lambs for a week. Scientists have developed an artificial womb that has been successfully used to incubate healthy baby lambs for a week.
This marks an advance that may one day be able to save the lives of extremely premature human babies.
Researchers from the University of Western Australia and Tohoku University Hospital in Japan sought to develop an effective treatment strategy for extremely preterm infants.
These include those born at the border of viability (22-23 weeks).
The research showed that preterm lambs were successfully maintained in a healthy, infection-free condition with significant growth.
This is for a period of one week using ex- vivo uterine environment (EVE) therapy.
With further development, EVE therapy could prevent the severe morbidity suffered by extremely premature infants by potentially offering a medical technology that does not currently exist.
At this gestational age the lungs are often too structurally and functionally under-developed for the baby to breathe easily.
For improving outcomes for this group would be to treat them as a foetus rather than a small infant.
The equipment is essentially is a high-tech amniotic fluid bath combined with an artificial placenta.
By providing an alternative means of gas exchange for the foetus, it prevents ventilation-derived injury.
This will help save the lives of those babies whose lungs are too immature to breathe properly," he said.
|
▼ NASA launches communications satellite TDRS-M [08-21-17]
 NASA’s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-M (TDRS-M). NASA’s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-M (TDRS-M).
This is the third and final in a series of next generation communications satellite.
It has successfully been placed into orbit following separation from a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket.
TDRS-M launched Friday at 8:29 a.m. EDT from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
Ground controllers report the satellite is in good health at the start of a four-month checkout in space by its manufacturer, Boeing.
NASA will conduct additional tests before putting TDRS-M into service early next year.
When ready, TDRS-M will become part of NASA’s Space Network providing navigation and high-data-rate communications to the International Space Station, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, rockets and a host of other spacecraft.
TDRS: Value
- The TDRS fleet is a critical connection delivering science and human spaceflight data to those who can use it here on Earth.
- TDRS-M will expand the capabilities and extend the lifespan of the Space Network, allowing us to continue receiving and transmitting mission data well into the next decade.
- The mission of the TDRS project, established in 1973, is to develop, launch and deliver data communications relay spacecraft to support Nasa’s Space Network.
- This provides high-data-rate communications and accurate navigation.
- The TDRS-M spacecraft is effectively identical—in both function and performance—to the TDRS-K and -L spacecraft launched in 2013 and 2014, respectively.
- The TDRS fleet began operating during the space shuttle era with the launch of TDRS-1 in 1983.
- Of the TDRS spacecraft launched to date, only two have been retired and five of the nine operational satellites have exceeded their design life.
- These continue to provide essential communications and navigation services.
- Nasa’s Space Communications and Navigation program, known as SCaN, is part of the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters in Washington, and is responsible for the Space Network.
- The TDRS project office at Goddard manages the TDRS development program.
- Management of the launch service for TDRS-M is the responsibility of NASA’s Launch Services Program based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Centre in Florida. ULA provided the Atlas V rocket launch service.
|
▼ Mobile apps for e-toll collection [08-18-17]
 National Highways Authority of India launched two mobile Apps - MyFASTag and FASTag Partner in New Delhi. National Highways Authority of India launched two mobile Apps - MyFASTag and FASTag Partner in New Delhi.
This is to facilitate the availability of FASTags for Electronic Toll Collection.
The cumbersome method of purchase and recharge of FASTags has been one of the major challenges with the ETC project.
The mobile Apps launched today will ease the process, making it possible to buy or recharge FASTags at the click of a mobile button.
MyFASTag is a consumer App that can be downloaded from the App Store for both Android and iOS systems.
A consumer can purchase or recharge FASTags on this App.
The App also helps to keep track of transactions and provides for online grievance redressal.
FASTag Partner is a merchant App.
Agencies like Common Services Centre, banking partners and vehicle dealers can sell and enrol FASTag through this App.
In addition to this, the App can also be used to activate the RFID tags that came built in with around 74 lakh cars in the country.
These RFID tags are already fixed on the cars but are dormant.
This App will convert these RFID tags into ETC Tag (FASTag).
Also dedicated FASTag lanes will become operational on all 371 NHAI toll plazas from 1st September 2017, he said.
Online sale of FASTags and offline sale through Common Services Centre (CSC) near toll plazas are also carried out.
FASTag can now be purchased online from Issuer Banks websites / NHAI website / IHMCL website and will be delivered by courier at the door step of the purchaser.
More than 6 lakh FASTags have been sold so far.
|
▼ Meet Malpelo - World's tectonic plate no. 57! [08-18-17]
 A team of researchers from Rice University in Texas have discovered a new tectonic plate off the coast of Ecuador. A team of researchers from Rice University in Texas have discovered a new tectonic plate off the coast of Ecuador.
There were 56 plates; now, there are 57 - and researchers think there could be one more to find.
By measuring the rates of seafloor spreading and the angles at which the plates slip by each other, researchers can estimate the speeds at which plates spin.
In this case, the velocity of the plates doesn't sum to zero at all, as is usual.
It sums to 15 millimetres a year, which is huge.
The scientists surmised a plate was missing from the equation.
To find its boundaries, researchers mined a catalogue of multi-beam sonar soundings.
Anomalies in the data suggested the presence of a new plate east of the known Panama transform fault, a region originally believed to be part of the Nazca plate.
A diffuse boundary is best described as a series of many small, hard-to-spot faults rather than a ridge or transform fault that sharply defines the boundary of two plates.
Earthquakes along diffuse boundaries tend to be small and less frequent than along transform faults.
Therefore there was little information in the seismic record to indicate this one's presence."
When researchers crunched the seafloor spreading and boundary angle numbers again, they still couldn't zero out their equation.
This suggests the possibility of another plate.
|
▼ Apples originated from Kazakhstan: Scientists [08-17-17]
 The modern crisp apple originated in a mountainous region of Kazakhstan, according to a study which reveals a surprising two-way journey on the Silk Road for one of the world’s most popular fruit. The modern crisp apple originated in a mountainous region of Kazakhstan, according to a study which reveals a surprising two-way journey on the Silk Road for one of the world’s most popular fruit.
As travellers journeyed east and west along the Silk Road, they brought with them apple seeds from the choicest fruit they took from wild trees, researchers said.
This early selection would eventually lead to the 7,500 varieties of apple that exist today
Researchers sequenced and compared the genomes of 117 diverse apple accessions, including Malus domestica and 23 wild species from North America, Europe, and east and central Asia.
They narrowed down the origin of the domesticated apple from very broad central Asia to Kazakhstan area west of Tian Shan Mountain.
Researchers discovered that the first domesticated apple had travelled to the east, hybridising with local wild apples along the way, yielding the ancestors of soft, dessert apples cultivated in China today.
Researchers also found that as the apple travelled west along the Silk Road, trees grew from dropped seeds and crossed with other wild apple varieties, including the sour European crabapple (Malus sylvestris).
They found that Malus sylvestris has contributed so extensively to the apple’s genome that the modern apple is actually more similar to the sour crabapple than to its Kazakhstan ancestor, Malus sieversii.
Kazakhstan: Know More
- Kazakhstan, a Central Asian country and former Soviet republic, extends from the Caspian Sea in the west to the Altai Mountains at its eastern border with China and Russia.
- Its largest metropolis, Almaty, is a long-standing trading hub whose landmarks include Ascension Cathedral, a Tsarist-era Russian Orthodox church, and the Central State Museum of Kazakhstan, displaying thousands of Kazakh artefacts.
- Capital: Astana
- Currency: Kazakhstani tenge
- Official languages: Kazakh, Russian
|
▼ After cardiac Stents, prices for knee implants capped [08-17-17]
 After giving relief to heart patients in February earlier this year by capping stent prices, this decision is likely to give relief to lakhs of patients suffering from old age and knee related problems. After giving relief to heart patients in February earlier this year by capping stent prices, this decision is likely to give relief to lakhs of patients suffering from old age and knee related problems.
Union Minister for Chemicals and Fertilizers Ananth Kumar briefed the media on the price capping and said that Rs 1500 crore spent by patients will now be saved.
As per the NPPA notification, the standard and most widely used complete knee implant (cobalt chromium) has been capped at INR 54,720 + GST.
The price has been reduced by 65 per cent. Hospitals were, until now, charging upto INR 1,58,324.
Total knee implant of special metals like Titanium and oxidised Zirconium has been capped at INR 76,600 + GST.
Hence, there is a reduction in price by 69 per cent. Earlier, the hospitals were charging upto INR 2,49,251.
Highly flexible implants have been capped at INR 56,490 + GST, which has seen a 69 per cent reduction. Hospitals used to charge upto INR 1,81,728 for such implants.
Second knee implant surgery would cost INR 1,13,950 + GST, hence there has been 59 per cent reduction.
It used to cost INR 2,76,869 earlier.
The NPPA has made it clear that no healthcare institutions such as hospitals/nursing-homes/clinics performing orthopedic surgical procedures using knee implants shall solicit any patient to purchase knee implants from it, in case, the patient is interested in procuring such implant from any other third-party sources.
In case the manufacturer supplies/sells knee implants directly to the orthopedic healthcare institutions, without involvement of any distributor, then the maximum trade margin for hospitals/nursing homes/clinics shall be restricted at 16 per cent.
|
▼ Injectable tissue bandage to mend damaged hearts [08-17-17]
 Scientists have developed an injectable tissue bandage smaller than a postage stamp that can repair damaged hearts. Scientists have developed an injectable tissue bandage smaller than a postage stamp that can repair damaged hearts.
Repairing heart tissue destroyed by a heart attack or medical condition with regenerative cells or tissues usually requires invasive open-heart surgery.
Researchers at the University of Toronto in Canada have developed a technique that lets them use a small needle to inject a repair patch, without the need to open up the chest cavity.
The AngioChip is a tiny patch of heart tissue with its own blood vessels and heart cells beating with a regular rhythm.
If an implant requires open-heart surgery, it’s not going to be widely available to patients.
|
▼ Zika plant based vaccine developed [08-16-17]
Scientists have developed the world's first plant-based Zika vaccine that may be more effective, safer and cheaper than other vaccines against the mosquito-borne virus.
Currently, there are no licensed vaccines or therapeutics available to combat Zika.
The vaccine developed by researchers from Arizona State University (ASU) in the US works against a part of a Zika viral protein, called DIII, that plays a key role for the virus to infect people.
All flaviviruses have the envelope protein on the outside part of the virus. It has three domains.
The domain III has a unique stretch of DNA for the Zika virus, and scientists exploited this to generate a robust and protective immune response that is unique for Zika.
The researchers first grew the envelope protein in bacteria, then prepared the DIII protein domain in tobacco plants.
The team then performed immunisation experiments in mice, which induced antibody and cellular immune responses that have been shown to confer 100 per cent protection against multiple Zika virus strains in mice.
The team's protein-based vaccine uses the smallest and most unique part of the Zika virus that can still elicit a potent and robust immune response.
A pseudovirus which is a fake virus displays only the DIII part of the envelope protein on the surface.
The vaccine produces a potent protective immune response, but also, that it does not produce antibodies that may be cross reactive for dengue, West Nile, yellow fever or others
Zika: Know More - The worldwide Zika threat first emerged in 2015.
- It was responsible for infecting millions as it swept across the Americas.
- It struck great fear in pregnant women, as babies born with severe brain birth defects quickly overburdened hospitals and public health care systems.
|
▼ New fruit bat nicknamed after Star Wars character Yoda [08-14-17]
 An unusual breed of fruit bat- previously nicknamed ‘Yoda’ due to its resemblance to the Jedi Master in the popular Star Wars movies - has now officially been registered as a new species. An unusual breed of fruit bat- previously nicknamed ‘Yoda’ due to its resemblance to the Jedi Master in the popular Star Wars movies - has now officially been registered as a new species.
Discovered in a remote rainforest of Papua New Guinea, the bat’s has been renamed the happy (Hamamas) tube - nosed fruit bat.
Its unusual features saw it affectionately referred to as the ‘Yoda bat’
However, after examining studies and some 3,000 specimens in 18 museums around the world, a researcher from the University of York in the UK has formally distinguished and registered the new species.
The species is very difficult to tell apart from other tube-nosed bat species.
Bat species often look similar to each other, but differ significantly in behaviour, feeding and history.
Most of the morphological characteristics that separate this bat from other species are associated with a broader, rounder jaw which gives the appearance of a constant smile.
The happy tube - nosed fruit bat’s formal name, Nyctimene wrightae, is after the conservationist Deb Wright, who devoted 20 years to building conservation programmes and long - term scientific capacity in Papua New Guinea.
Nyctimeninae were one of the first species of bat described in records dating back to 1769, and later in 1860 Alfred Russel Wallace - British naturalist and one of the fathers of evolution - collected two further species.
The bats’ tube noses, bright colours, thick stripe on the back and spots have attracted attention for some 250 years, but researchers are still finding new hidden species in the group.
There were no illustrations of the cyclotis group of bats which made identifying bats really difficult.
So difficult was it that Papua New Guinea produced stamps illustrating the bats but could not allocate a species name.
Now, with photographs, illustrations and a key of the other species in the group, it makes it possible to distinguish between three species of the group.
Fruit bats are crucial to rainforest health, pollinating and dispersing many tree species, therefore it is essential we know what is there and how we can protect it.
|
▼ National Cyber Coordination Centre goes live [08-11-17]
 National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC), the government’s cyber security project which scans and records meta data on the Internet is live. National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC), the government’s cyber security project which scans and records meta data on the Internet is live.
This is according to P.P Chaudhary, Minister of State for Electronics and IT (Meity).
The NCCC received an in-principal approval from the Cabinet in May 2013,
It “screens all forms of meta-data, ensure better coordination between various intelligence agencies and streamline intelligence gathering”, the report pointed out.
The project costs INR 500 crore and implemented by Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In).
Data NCCC Covers
- The NCCC can “actively” tie up with other cyber intelligence agencies to collect and share data to conduct surveillance, although, via lawful means.
- The NCCC is limited to online and cyber intelligence and collects data through tie ups with other intelligence units. The government’s meta data scanner is likely to have access to:
- The National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) which keeps all sorts of citizen data in a single database that can be accessed by officers from RAW, CBI, IB etc. NATGRID and NCCC were proposed under the same ministry initially and it’s likely that there is some amount of cross-data sharing. NATGRID has access to hold 21 categories of citizen database like bank account details, telephone records, passport data and vehicle registration details. NATGRID has access to this data in real-time and through tie up with various ministries and departments called provider agencies and 11 other intelligence and investigative agencies.
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), Intelligence Bureau (IB), the National Investigation Agency (NIA), the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) and the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) also come under the MHA [More on this here]. Data from these intelligence units are also likely to be picked by the NCCC.
- The New Media Wing (NMW) and the Electronic Media Monitoring Centre (EMMC)-wings that are involved in media surveillance - housed under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) are also involved in media surveillance and shares data with other intelligence units.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) which is focused on national security matters, also shares and gathers information with the intelligence departments similar to NCCC and is also likely to be an information provider.
Other Cyber Surveillance Projects- Cyber Swachhta Kendra is the Government’s malware and bot-net cleaning centre were set up in February this year.
- Named as ‘Cyber Swachhta Kendra’, the project has tie ups with ISPs, academia, banks and anti-virus companies to provide citizens with tools to protect data on laptops, computers and mobile phones.
- In December 2015, the Government of India set up the ‘Indian Cyber Coordination Centre’ (I-4C), which helps in monitoring cyber crimes, offences such as child pornography, cyber bullying, as well as helping law enforcement agencies in curbing these crimes.
|
▼ HySIS: New earth observation satellite from ISRO [08-11-17]
 A new set of future satellites called hyperspectral imaging satellites is set to add teeth to the way India will be seen from about 600 km in space. A new set of future satellites called hyperspectral imaging satellites is set to add teeth to the way India will be seen from about 600 km in space.
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) says it plans to launch a full-fledged niche earth observation (EO) satellite - called the Hyperspectral Imaging Satellite or HySIS - using a critical chip it has developed.
There is no specific time-frame yet for its launch, an ISRO spokesman said, adding that meanwhile, the new chip, technically called an “optical imaging detector array,” that they have created for it would be tested and perfected.
ISRO is endeavouring to enter the domain of operational hyperspectral imaging from earth orbit with a satellite that can see in 55 spectral or colour bands from 630 km above ground
Hyspex Imaging: Know More
- Hyperspectral or hyspex imaging is said to be an earth observation trend that is being experimented globally.
- Adding a new dimension to plain-vanilla optical imagers, it can be used for a range of activities from monitoring the environment, crops, looking for oil and minerals all the way up to military surveillance - all of which need images that show a high level of differentiation of the object or scene.
- About a decade ago, ISRO added another earth observation niche with microwave or radar imaging satellites RISAT-1 and 2 that could ‘see’ through clouds and the dark - an important feature useful for the military and security agencies.
- ‘Hyspex’ imaging is said to enable distinct identification of objects, materials or processes on earth by reading the spectrum for each pixel of a scene from space
ISRO first tried it out in an 83-kg IMS-1 experimental satellite in May 2008. The same year, a hyperspectral camera was put on Chandrayaan-1 and used to map lunar mineral resources. - Very few space agencies have such a satellite; a German environmental satellite called EnMAP is due to be launched on an Indian booster in 2018.
- The payloads development centre, Space Applications Centre, Ahmedabad, designed the architecture of the chip which was made at ISRO’s electronics arm, the Semi-Conductor Laboratory, Chandigarh. The result was a detector array that could read 1000 x 66 pixels.
- Hyspex is an evolving technology
|
▼ Biosphere reserve total 18 in India [08-9-17]
 Biosphere Reserve (BR) is an international designation by UNESCO for representative parts of natural and cultural landscapes extending over large area of terrestrial or coastal/ marine ecosystems or a combination thereof. Biosphere Reserve (BR) is an international designation by UNESCO for representative parts of natural and cultural landscapes extending over large area of terrestrial or coastal/ marine ecosystems or a combination thereof.
BRs are designated to deal with one of the most important questions of reconciling the conservation of biodiversity, the quest for economic and social development and maintenance of associated cultural values.
BRs are thus special environments for both people and the nature and are living examples of how human beings and nature can co-exist while respecting each other’s needs.
There are 18 Biosphere Reserves in the country.
The Biosphere Reserve Programme is guided by UNESCO Man and Biosphere (MAB) programme as India is a signatory to the landscape approach supported by MAB programme.
A scheme called Biosphere Reserve is being implemented by Government of India since 1986, in which financial assistance is given in 90:10 ratio to the North Eastern Region States and three Himalayan states.
It is in the ratio of 60:40 to other states for maintenance, improvement and development of certain items.
The State Government prepares the Management Action Plan which is approved and monitored by Central MAB Committee”.
LIST OF BIOSPHERE RESERVES
1. Agasthyamala, Karnataka-Tamil Nadu-Kerala
2. Nilgiri, Tamil Nadu-Kerala
3. Gulf of Mannar, Tamil Nadu
4. Great Nicobar, Andaman & Nicobar Island
5. Seshachalam, Andhra Pradesh
6. Sundarban, West Bengal
7. Similipal, Odisha
8. Kachchh, Gujarat
9. Achanakmar-Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh-Chattisgarh
10. Pachmarhi, Madhya Pradesh
11. Panna, Madhya Pradesh
12. Nokrek, Meghalaya
13. Dibru-Saikhowa, Assam
14. Manas, Assam
15. Dehang-Debang, Arunachal Pradesh
16. Khangchendzonga, Sikkim
17. Nanda Devi, Uttrakhand
18. Cold Desert, Himachal Pradesh
|
▼ Scientists rewrite Neanderthal history [08-9-17]
A new way to use DNA to peer into the history of humanity is rewriting what experts know about our long-extinct cousins, the Neanderthals, US researchers found on 7th Aug 2017.
Previous research has suggested that near the end of their existence some 40,000 years ago, only about 1,000 Neanderthals were left on Earth.
But the new study shows their population was far larger - likely numbering in the tens of thousands - though they existed in isolated groups across Europe.
The genetic clues include Neanderthal DNA that contains mutations that usually occur in small populations with little genetic diversity.
Also, Neanderthal remains - found in various locations - are genetically different from each other.
The idea is that there are these small, geographically isolated populations, like islands, that sometimes interact, but it’s a pain to move from island to island.
Using a new method to analyse DNA sequence data, researchers also found that Neanderthals split from another mysterious lineage, known as the Denisovans, about 7,44,000 years ago.
This is much earlier than any other estimation of the split.
After that, the global Neanderthal population grew to tens of thousands.
Very little is known about the Denisovans, sometimes described as the Eastern cousins of Neanderthals.
Only a few pieces of their remains - including some teeth and a pinkie bone - have ever been found.
Both Denisovans and Neanderthals mated with the ancestors of modern humans, who emerged from Africa about 60,000 years ago.
Researchers are not sure exactly why Neanderthals or Denisovans eventually died out, but it could have been due to harsh climate, or competition for scare resources with modern humans.
The study was based on comparing the genomes of four human populations: Modern Eurasians, modern Africans, Neanderthals and Denisovans.
This improved statistical method, called legofit, helped researchers estimate the percentage of Neanderthal genes flowing into modern Eurasian populations.
This they confirmed was about 2%.
The method revealed the date at which these ancestral populations diverged from each other, and their population sizes.
|
▼ Two new species of plants from Jurassic period found! [08-8-17]
 Research conducted on a tree found in the Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden in West Bengal has revealed two new species of Cycas to the world. Research conducted on a tree found in the Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden in West Bengal has revealed two new species of Cycas to the world.
Cycas are one of the most ancient plants whose fossils date to the Jurassic period and are often referred to as “living fossils”.
While initial studies on the lone tree revealed that it was Cycas, a gymnosperm, further research based on its morphological and anatomical characters led to the discovery of new species of Cycas pschannae and, later, Cycas dharmrajii in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
The species were named after scientists Paramjit Singh Channa and Dharmraj S. Mishra.
This discovery takes the number of Cycas species found in the country to 14.
“The lone Cycas pschannae found in the Botanic Garden may have been planted by the British.
Cycads are very slow growing trees and this particular tree did not catch much attention before 2001 when we started working on it.
Of the nine locations where the species was found, it was only at two places that a congregate population of significant adult plants could be located, Mr. Singh said.
The scientists found about 1,200 plants at Middle Andaman Curt Burt Bay Wildlife Sanctuary, which included only 13 adult trees and 500 in North Andaman, Ross Island which also had 13 adults.
In the rest of the places the population of the new species was scattered with very few adult plants.
It was while hunting for Cycas pschannae that the scientist laid his eyes on Cycas dharmrajii in Table Excelsior Island.
Cycas dharmrajii, whose morphological and anatomical details were made public in the Nordic Journal of Botany in April, is characterised by the abnormal branching habit of its giant trunk and its swollen base.
Unique features of Newly Discovered Cycas
- What makes the Cycas dharmrajii distinct from other Cycas found in the country is the well-defined 10 to 28 hook-like structures in the apex of the mega sporophyll (sporophyll are spore-bearing leaf-like female sex organ of the plant).
- The sporophylls of Cycas pschannae are characterised by the presence of two lateral horn-like structures.
According to scientists, Cycas evolved on the earth as the first seeded plants and they grow very slowly, adding only a few centimetres every year. - Nearly 65% of Cycas are threatened but what makes the flora unique is that despite being a contemporary of the dinosaur, the genus continues to thrive.
- There are over 100 species of Cycas found across the globe.
|
▼ IISc researchers discover CO sensor. [08-8-17]
 Indian Institute of Science researchers have developed a highly sensitive nanometre-scale carbon monoxide sensor by employing an innovative fabrication technique. Indian Institute of Science researchers have developed a highly sensitive nanometre-scale carbon monoxide sensor by employing an innovative fabrication technique.
It is known that carbon monoxide (CO) can have adverse effects on the health of people exposed to it. Hence, it becomes necessary to have good, low-cost carbon-monoxide sensors.
Typically, a sensor would be a thin, current carrying plate whose resistance changes on exposure to carbon monoxide.
This in turn changes the value of the current flowing through it. This change when measured indicates the level of carbon monoxide in the air.
Most available sensors are in the micrometer range, a nanometer-sized detector would have a higher sensitivity, but the cost of manufacturing it goes up as the size decreases.
This is where the work of C.S. Prajapati and coworkers of Indian Institute of Science comes in.
To build this zinc-oxide (ZnO) nanostructure on a silicon wafer substrate, the researchers first placed tiny polystyrene beads on the wafer.
These beads arrange themselves into what is called a hexagonal close-packed structure on the oxidised silicon wafer.
Maintaining a reasonable level of vacuum, a high voltage is applied which “etches away” the surfaces of the beads until a gap of desired thickness is formed between adjacent beads.
Then zinc oxide is deposited on the system.
This occupies the spaces between the beads, forming a honeycomb like nano-mesh that can function as a nanosenor.
Scaling down from 10 micrometer feature size to 10 nanometer feature (used in this work) can enhance the efficiency 1,000 times.
However, the development cost of nanostructured gas sensors using existing lithography tools is really very high, which eventually impacts the overall cost of the device.
This device is also easy to scale for mass production.
Nanostructure-based gas sensors are very promising in their performance due their high surface-to-volume ratio. The existing techniques to create honeycomb nanostructures using photolithography and e-beam lithography are expensive and time-consuming.
The proposed technique can potentially reduce the cost by more than 50%.
If these sensors were at traffic intersections, we can do real time mapping of pollution hot-spots in a city.
This would be an enabler in realizing smart cities.
|
▼ All women IIT team discovers new drug delivery for bacterial infections [08-8-17]
 An all-women team of researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi has developed a new drug delivery platform, using nanoparticles, which they say will more effectively target bacterial infections. An all-women team of researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi has developed a new drug delivery platform, using nanoparticles, which they say will more effectively target bacterial infections.
This is improving chances of recovery from cancer-related secondary infections.
The team consists of two faculty members - Neetu Singh from the Centre for Biomedical Engineering and Shalini Gupta from the Department of Chemical Engineering - and their students Smita Patil and Rohini Singh.
The nanotechnology-based delivery system would be specifically useful for cancer patients because if the bacterial infection in cancer remains untreated, it can infect the host even after the cancer cells are killed by chemotherapy.
The scientists are focusing not on mammalian cells, but on bacteria which slip into the cancer cells.
|
▼ Hot Jupiter may have stratosphere! [08-8-17]
 Discovered in 2016 by astronomers at the WASP-South survey, WASP-121b is 1.87 times bigger than Jupiter and 1.18 times more massive. Discovered in 2016 by astronomers at the WASP-South survey, WASP-121b is 1.87 times bigger than Jupiter and 1.18 times more massive.
Its host star, WASP-121 (TYC 7630-352-1), is an active F6-type main-sequence star about 1.5 times the size of the Sun.
The WASP-121 system is located 881 light-years away in the constellation Puppis.
WASP-121b is a so-called ‘hot Jupiter’ and takes just 1.3 days to orbit WASP-121. It is so close to the parent star that if it got any closer, the star’s gravity would start ripping it apart.
Astronomers estimate the planet’s temperature to be about 4,600 degrees Fahrenheit (2,500 degrees Celsius), hot enough to boil some metals.
Previous research found possible signs of a stratosphere on WASP-33b as well as some other hot Jupiters.
The new study presents the best evidence yet because of the signature of hot water molecules that astronomers observed for the first time.
This result is exciting because it shows that a common trait of most of the atmospheres in our solar system - a warm stratosphere - also can be found in exoplanet atmospheres.
Theoretical models have suggested stratospheres may define a distinct class of ultra-hot planets, with important implications for their atmospheric physics and chemistry.
These observations support this picture.
To study the stratosphere of WASP-121b, the team observed a secondary eclipse of the planet using the Wide Field Camera onboard the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and the Infrared Array Camera onboard NASA’s Spitzer space telescope.
The researchers analysed how different molecules in the stratosphere react to particular wavelengths of light.
Water vapour in the planet’s atmosphere, for example, behaves in predictable ways in response to certain wavelengths of light, depending on the temperature of the water.
Starlight is able to penetrate deep into a planet’s atmosphere, where it raises the temperature of the gas there.
This gas then radiates its heat into space as infrared light.
However, if there is cooler water vapour at the top of the atmosphere, the water molecules will prevent certain wavelengths of this light from escaping to space.
But if the water molecules at the top of the atmosphere have a higher temperature, they will glow at the same wavelengths.
The emission of light from water means the temperature is increasing with height.
In Earth’s stratosphere, ozone gas traps ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, which raises the temperature of this layer of atmosphere.
Other solar system bodies have stratospheres, too; methane is responsible for heating in the stratospheres of Jupiter and Saturn’s moon Titan, for example.
In solar system planets, the change in temperature within a stratosphere is typically around 100 degrees Fahrenheit (about 56 degrees Celsius).
On WASP-121b, the temperature in the stratosphere rises by 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit (560 degrees Celsius).
The astronomers do not yet know what chemicals are causing the temperature increase in WASP-121b’s atmosphere.
Vanadium oxide and titanium oxide are candidates, as they are commonly seen in brown dwarfs.
Such compounds are expected to be present only on the hottest of hot Jupiters, as high temperatures are needed to keep them in a gaseous state.
|
▼ NABI - India's first Agri-Food and Nutritional based Biotechnology Institute [08-7-17]
 Dr. Harsh Vardhan, Union Minister for Science & Technology & Earth Sciences, Environment, Forest & Climate Change inaugurated the new Administrative and Research Buildings of two national institutes under the administrative control of Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology. Dr. Harsh Vardhan, Union Minister for Science & Technology & Earth Sciences, Environment, Forest & Climate Change inaugurated the new Administrative and Research Buildings of two national institutes under the administrative control of Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology.
Government of India set up two institutes namely National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) and Centre of Innovative and Applied Bioprocessing (CIAB) in Mohali, Punjab.
These institutes with state of the art equipment will enables scientists/students to exploit the biotechnological tools to address the problems related to quality of food and malnutrition with full enthusiasm and zeal.
It will aim towards getting inspiration from the legacy and contributions of champions in the field of science and technology.
Both the institutes are to address the problems of hunger & malnutrition and to bring nutritional revolution in the country through biotechnology research and innovation for Food and Nutrition Security.
NABI is the first Agri-Food and Nutritional based Biotechnology Institute, which has been set up by the Dept. of Biotechnology in the Knowledge City, Sector 81, Mohali.
CIAB has been set up adjacent to NABI and is the first institute dedicated to generation of secondary agriculture bioproducts through value addition to unutilised and underutilised biomass.
Both the institutes area part of agri-food cluster in the Knowledge City, Mohali along with its neighbouring institutes, like; IISER, ISB, INST and Biotech Park.
The campus comprises of laboratory buildings, 15 acres of land for field experiments, a large glass house, transgenic net houses, office area, housing, guest house, research scholar hostel, utilities and other requisite services.
Total entire area of the campus is 50 acres.
The building complex of CIAB has a total floor space of 77000 square feet built at a cost of INR Forty three crores whereas NABI has a total floor space of 3,17,500 square feet built at a cost of INR one hundred and thirty five crores.
The institutes apart from providing quality research in the field of agricultural biotechnology and bio processing also provide innovative technologies in the field of food processing.
NABI is playing an important role in conducting motivational course to the students of local schools to increase their awareness in life sciences.
Their products of nutritionally rich crops and processing of crop residues in useful products will be provided to the local farming communities to increase their income.
The industry ready specialized products like high anthocyanin have already been taken by local industries under specific MOU.
They are acting as nodal agencies for local organization in the areas Agri food and nutritional biotechnology.
|
▼ ISTRAC, ISRO, CSIR, NPL sign MoU [08-7-17]
 A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the ISRO Telemetry Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Department of Space and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)-National Physical Laboratory (NPL), Ministry of Science and Technology, in New Delhi. A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the ISRO Telemetry Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Department of Space and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)-National Physical Laboratory (NPL), Ministry of Science and Technology, in New Delhi.
The MoU provides for time and frequency traceability services to ISRO by CSIR-NPL
The scope of this MoU is the rendering by CSIR-NPL, of all the necessary actions, necessary to support the following:
- Time and Frequency Traceability services from National Time Scale of CSIR-NPL to IRNWT-I and IRNWT-II of ISTRAC/ISRO through Two-way Satellite Time and Frequency Transfer (TWSTFT).
- Time and Frequency Traceability services from National Time Scale of CSIR-NPL to IRNWT-I and IRNWT-II of ISTRAC/ISRO through GNSS CV.
- Annual audit of IRNWT-I and IRNWT-II as per ISO/IEC 17025 for ensuring correctness and accuracy of the time traceability.
The MoU came into force from date of signing of the agreement in Aug 2017 and shall remain valid for a period of 5 years thereafter. Subsequently, the MoU will be renewed on mutual agreement between CSIR-NPL and ISTRAC/ISRO. Scientists of two premier scientific institutions, NPL and ISRO, have made great efforts in this direction and he applauded them for their contribution. This is very important landmark and an occasion to acknowledge the great contribution of our scientists. NPL has one of the five Atomic Clocks in India and the people should be encouraged to visit the laboratories and understand science and its contribution to the development of the country. The main success of Department of Space is that India has consistently widened the space technology use to various fields. ISRO has achieved many milestones in the recent past e.g. successful launching of highest number of satellites, completion of 1,000 days of Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), launch of South Asia Satellite etc. ISRO has already signed MoUs with various ministries and departments which is contributing to the social applications of space technology. The ISRO has signed MoU with Ministry of Agriculture for Geo-MNREGA, with Ministry of Railways for guarding the railway crossings. ISRO is also contributing to the Smart City Programme and other initiatives.
|
▼ Scientists develop silk mat to combat arthritis [08-7-17]
 Scientists from IIT Guwahati have synthesised mats made of silk-proteins and bioactive glass fibres that they believe can assist the growth of bone cells and repair worn-out joints in arthritis patients. Scientists from IIT Guwahati have synthesised mats made of silk-proteins and bioactive glass fibres that they believe can assist the growth of bone cells and repair worn-out joints in arthritis patients.
The disease most commonly affects joints in the knees, hips, hands, feet, and spine and is marked by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bones.
Left untreated, it can cause severe pain, swelling, and eventually limited range of movement.
Current clinical treatment methods are limited by lack of viable tissue substitutes to aid the repair process
To develop a suitable tissue substitute, scientists looked into the natural bone-cartilage interface and tried to mimic it synthetically in lab conditions.
Knee osteoarthritis is the most common bone and joint disease in India. The available clinical grafts were expensive.
The scientists used silk, a natural protein to fabricate electro-spun mats to mimic the cartilage portion and bioactive glass to develop a composite material, similar to the natural tissue.
For the mat, scientists used a kind of silk easily available in northeast India.
Muga [Assam] silk is endowed with properties that enhance the healing process.
The researchers adopted a green fabrication approach for the developing the silk composite mats - electrospinning.
It is similar to knitting, except that it utilises electric high-voltage force to draw ultrafine fibres.
A layer by layer approach was followed, where the bone layer was first formed, on top of which the cartilage layer was developed.
The resulting composite mat resembled the architecture of the bone-cartilage interface.
To assist the regenerative process, the mats would be grafted in the defected joint with cells harvested from the patient.
|
▼ NavIC: Indigenous regional positioning system [08-4-17]
 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has deployed an indigenous regional positioning system named as “Navigation with Indian Constellation” (NavIC). Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has deployed an indigenous regional positioning system named as “Navigation with Indian Constellation” (NavIC).
It consists of seven satellites in a constellation to provide Position, Navigation and Timing (PNT) services in Indian mainland and surrounding region up to 1500 Km.
It provides two types of services viz. Standard Positioning Service (SPS) and Restricted Service (RS).
A budget of INR 1420 Crore has been approved by the Government for the realisation of the system including 7 in-orbit satellites, 2 satellites as ground spare and associated ground segment.
ISRO has established the required space segment of the NavIC system for providing signal in space enabling position, navigation and timing information and it can support commercial civil applications.
Indian entrepreneurs are being enabled for providing services through NavIC receiver system and requisite information has been made available in public domain.
The demonstrations for vessel tracking, vehicle tracking, messaging services for fishermen, timing applications have been conducted.
Mobile-Apps for navigational alerts across maritime jurisdictions is developed and tested for the Fishermen community using first generation NavIC receivers.
Various types of user receivers are being developed indigenously involving Indian industry and discussions amongst government departments, user-receiver manufacturers, system integrators and service providers are taking place for the usage of NavIC system.
While the space and ground segment of the NavIC system has been established and demonstrations of various applications/ services have been conducted, the time required for it to become fully operational depends on the service providers making the services available in the market.
It may take couple of years to become fully operational in the market
|
▼ Partial eclipse on Raksha Bandhan [08-4-17]
 A partial eclipse of the Moon will occur on August 7,2017 which will begin from h. 22-52 IST and will continue upto h. 00-49 IST on August 8, 2017. A partial eclipse of the Moon will occur on August 7,2017 which will begin from h. 22-52 IST and will continue upto h. 00-49 IST on August 8, 2017.
Only a small fraction of the Moon will come under Earth’s shadow at maximum eclipse. This partial eclipse will be visible from all places of India.
The eclipse will be visible in the region covering Western Pacific Ocean,Oceania, Australia, Asia, Africa, Europe and Antarctica.
The entire partial eclipse will be visible from central and east Africa, central Russia, China, India , the Far East and most of Australia.
The places from where the beginning of the umbral phase will be visible at the time of moonset are western parts of North Pacific Ocean and South Pacific Ocean.
The places from where the ending of umbral phase will be visible at the time of moonrise are north western part of Africa, eastern parts of Spain, France and Germany.
The circumstances of the eclipse are as follows:
Eclipse will begin at 10:52 pm, reach the middle phase at 11:51 and close at 12:49 am.
Magnitude of the eclipse = 0.251 (Moon’s diameter being taken as 1.0)
Duration of the eclipse: 1 h 57 m.
The next eclipse of the Moon will occur on January 31, 2018, which will be a total lunar eclipse and will be visible from India.
|
▼ Venus - Israel launches first exploration satellite [08-4-17]
 Israel’s first exploration satellite, Venus, was successfully launched on a Vega launcher on Aug 2, 2017 at the Guiana Space Center’s Kourou site. Israel’s first exploration satellite, Venus, was successfully launched on a Vega launcher on Aug 2, 2017 at the Guiana Space Center’s Kourou site.
The country’s first environmental satellite is a major project of the Israel Space Agency and the French space agency CNES.
It was launched together with the OPTSAT3000, an advanced observation satellite designed for use by the Italian Defense Ministry.
Venus is another testament to Israel’s vast technological capabilities in all fields, and they are a force of science, technology and space with which the whole world wants to cooperate.
The findings that will be sent by the satellite will include data on the environment, agriculture, water and food.
Environmental satellites have become very important in recent years because of problems on Earth resulting from crowding of the population, the decline in space for agriculture and raising food, pollution and natural disasters.
Venus, which is the smallest satellite of its kind in the world, was built in the last few years by IAI.
It will observe fields and nature from space for environmental research and monitor land conditions, forestry, agriculture, the quality of water sources and more.
The mini-satellite is equipped with a special camera that can visualize details on Earth that are not visible to the naked eye.
It will take photos of set locations in Israel and round the world and provide researchers with scores of images daily, each of which will cover 760 sq.km.
It will revolve around the Earth 29 times within 48 hours and repeat exact photo angles, making it possible to note differences in conditions - characteristics that make the satellite unique, said the ministry.
Venus: Know More
- Weighing only 265 kg., Venus reached its position of 720 km. above Earth within 37 minutes and 18 seconds.
- The first sign with preliminary data was received on the ground five-and-a-half hours after launch, but the initial images will arrive a week later.
- Processed images will be sent to users three months after launch. Venus is due to remain in operation for 4.5 years, after which it will be shifted to a lower trajectory.
- Some 110 research areas will be photographed around the world. When the satellite passes over Israel, Venus will photograph three swaths in the Galilee, the coastal area and the Negev where most national parks, forests, ecological stations and nature areas exist.
- The photos will also benefit university, government and state research institutes.
- Although Venus is a joint project of Israel and France, all of the satellite’s hardware components were developed in Israel’s space industries.
|
▼ 17 percent of India's population has smartphones: Digital Evolution Index 2017 [08-2-17]
 India is making slow progress on covering the gap between “smart” and “feature” phones, according to a study, which said only 17 per cent of the Indian population owned a smartphone in early 2016. India is making slow progress on covering the gap between “smart” and “feature” phones, according to a study, which said only 17 per cent of the Indian population owned a smartphone in early 2016.
While cellphone pick-up is strong, the gap between “smart” and “feature” phones in circulation is wider than ever before, according to ‘Digital Evolution Index 2017’, a study by the Fletcher School at Tufts University in partnership with MasterCard.
India’s stubborn cash economy meant it took demonetisation by government decree to wean Indians away from notes and coins – an event that saw mobile wallet provider Paytm claim 170 million users in just a few months.
India is an interesting example of a nation with a growing mobile internet gap. The country has been adding more mobile subscriptions and fewer mobile internet subscriptions.
Only 17 per cent of the Indian population owned a smartphone in early 2016.
India has done a great job of adding more mobile users, but the country is tapering off its broadband, which presents a challenge.
It is not a problem of availability – it’s a vast country and the most vibrant telecom market in the world. But affordability remains an issue.
The study also noted the popularity of services like M- Pesa, rooted in older technology but demonstrating the potential for growth through data-enabled mobile solutions in India as well as across Africa.
M-Pesa, a money transfer service launched in 2007 in Kenya, has spread across Africa, India and parts of Eastern Europe.
Digital Evolution Index 2017: Know More
- The Fletcher School at Tufts University in partnership with Mastercard, unveiled the Digital Evolution Index 2017.
- This Index is a comprehensive research that tracks the progress countries have made in developing their digital economies and integrating connectivity into the lives of billions.
- The Index measures four key drivers – supply, consumer demand, institutional environment, and innovation.
- India has featured among 60 nations on Digital Evolution Index 2017, exhibiting a high potential in terms of digital payments.
|
▼ Meet the world's smallest spacecraft Sprites [08-1-17]
 Scientists have announced that the world’s smallest spacecrafts dubbed as Sprites ever launched are successfully travelling in low Earth orbit and communicating with systems on Earth. Scientists have announced that the world’s smallest spacecrafts dubbed as Sprites ever launched are successfully travelling in low Earth orbit and communicating with systems on Earth.
The six prototypes of Sprites were launched in June 2017 as part of the Breakthrough Starshot project designed to test technologies that would eventually be used for interstellar missions.
They are smallest spacecraft that have managed to establish contact with ground stations.
Sprites have been developed by researchers at Cornell University.
Each of the mini Sprite spacecrafts are built on a single 3.5*3.5 centimeter circuit board.
They weigh just four grams each.
They are equipped with tiny solar panels and two antennas, plus a tiny radio, computer, magnetometer (to orient to Earth’s magnetic field) and gyroscope (to move and stabilize the craft).
Sprites Mission: Know More
- The mission was designed to test the performance of the Sprites’ electronics when in orbit.
- It will also demonstrates their novel radio communication architecture.
- It will also explore the concept of solar sail propulsion in which spacecraft can be powered using only the sun’s radiation.
- These tiny satellites also mark the next step in the field of spacecraft miniaturization that can contribute to the development of centimetre and gram-scale StarChips envisioned under the Breakthrough Starshot project.
- Breakthrough Starshot is a comprehensive space program launched under the US $100 million Breakthrough Initiatives, announced by Yuri Milner and Stephen Hawking to develop and launch practical interstellar space missions.
- The program aims to demonstrate proof of concept for light-propelled spacecraft that could fly at 20 per cent of light speed.
- Its main objective is to send one-gram chips to star systems beyond the solar system in search of extraterrestrial intelligence.
|
▼ Scientists develop bio-glue for healing wounds [08-1-17]
 Scientists have developed a super strong, flexible Bio-glue for wound healing without causing toxicity. Scientists have developed a super strong, flexible Bio-glue for wound healing without causing toxicity.
It has been inspired by an adhesive material (glue) secreted by slugs that sticks to biological tissues
Slugs naturally secrete a special kind of mucus (adhesive material) in its place when threatened, making it difficult for a predator to pry it off its surface.
The bio-glue is double-layered hydrogel consisting of an alginate-polyacrylamide matrix supporting an adhesive layer that has positively-charged polymers protruding from its surface.
It bonds to biological tissues via three mechanisms – electrostatic attraction to covalent bonds between neighbouring atoms, negatively charged cell surfaces and physical interpenetration.
This bond makes the adhesive super strong.
It is the combination of a very strong adhesive force and has ability to transfer and dissipate stress.
It can bind to tissues with strength comparable to the body’s own resilient cartilage.
|
▼ Gelator: New hydrophobic material for oil spills [08-1-17]
 Scientists from the Indian Institute of Science, Education and Research (IISER), Thiruvananthapuram have developed gelator that can suck up oil and congeal it. Scientists from the Indian Institute of Science, Education and Research (IISER), Thiruvananthapuram have developed gelator that can suck up oil and congeal it.
The gelator is hydrophobic material that has property of oleilophilic (oil-loving) and takes up oil when it comes in contact with it.
It can be used to recover marine oil spills with a simple, efficient and cost-effective method.
The gelator is developed using a cheap raw material mannitol and cellulose pulp through a one-step process.
In this process the mannitol gets adsorbed on the cellulose fibre through hydrogen bonding. The adsorption process changes the cellulose matrix from being very hydrophilic (water-loving) to hydrophobic (water repelling).
The property of gelator to self-assemble to form micro fibres makes congealing of oil possible and the oil loses its fluidity and gets trapped within the entangled fibrous network to form a rigid gel.
Gelation essentially turns the liquid oil into semi-solid and this allows congealed oil to be simply scooped out using a scoop or a sieve.
The gelator was able to absorb and congeal 16 times its own weight of oil.
The absorbed oil can be recovered by applying pressure or fractionated by a simple distillation process.
|
▼ Reel life inspires real with discovery of compound BaZnGa [08-1-17]
 Scientists have created a compound inspired by the catchphrase “Bazinga” that is frequently uttered by Sheldon Cooper, a character on the popular TV series The Big Bang Theory. Scientists have created a compound inspired by the catchphrase “Bazinga” that is frequently uttered by Sheldon Cooper, a character on the popular TV series The Big Bang Theory.
The compound BaZnGa, made of barium (Ba), zinc (Zn) and gallium (Ga), forms a never-before-seen crystal structure.
However, BaZnGa did not have any other exciting features, scientists said.
It behaves like other non-magnetic quasicrystals, but has a different arrangement of atoms.
Its creation is part of scientific efforts to discover new materials and characterise them.
The researchers, who were already planning to study three-part compounds that contained barium and zinc, went ahead to create BaZnGa, after they watched a promo of the sitcom.
|