Object oriented analysis questions for Computer Science and MCA students
What are the steps to be followed to create CRC models?
What is CRC models?- CRC model stands for Class Responsibility Collaborator Model.
- It is a collection of standard index cards that have been divided into three sections:
I. Class Name
II. Responsibilities
III. Collaborators
| Class Name |
| Class Name | Collaborators |
- A 'Class name' represents a collection of similar objects.
- A 'Responsibility' is something that a class knows or does.
- A 'Collaborator' is another class that a class interacts with to fulfill its responsibilities.
- It is used in the design of object oriented software.
- It is a collection of CRC cards that represent whole or part of an application or problem domain.
Steps to create CRC models
Following are the steps of CRC model:
1. Find Classes
2. Find Responsibilities
3. Define Collaborators
4. Define Use-Cases
5. Arrange the cards on the table
1. Find Classes- Look for anything that interacts with the system, or is a part of the system.
- Look for reports generated by the system.
- Look for any screens used in the system.
- Immediately prototype interface and report classes.
- Look for the three to five main classes right away.
- Create a new card for a class immediately.
- Use one or two words to describe the class.
- Class names are singular.
2. Finding Responsibilities- Ask yourself what the class knows.
- Ask yourself what the class does.
- If you have identified a responsibility, ask yourself what class it "belongs" to?
- Sometimes get responsibilities that we won’t implement, and that’s OK.
- Classes will collaborate to fulfill many of their responsibilities.
3. Defining Collaborators- Collaboration occurs when a class needs information that it doesn’t have.
- Collaboration occurs when a class needs to modify information that it doesn’t have.
- There will always be at least one initiator of any given collaboration.
- Sometimes the collaborator does the bulk of the work.
- New responsibilities may be created to fulfill the collaboration.
4. Defining Use-Cases- The BDEs will identify them as the responsibilities of actor classes.
- Transcribe the scenarios onto cards.
5. Arrange the cards on the table- Cards that collaborate with each other should be close to one another on the desk.
- The more that two cards collaborate, the closer that they should be on the desk.
- Expect to be moving the cards around a lot at the beginning.
- Put "busy" cards towards the center of the table.
- People will identify relationships/associations between classes as they move them around.
Advantages of CRC Models- It breaks down communication barriers.
- It is simple and straightforward.
- It is non-threatening to users.
- It is inexpensive and portable.
Disadvantages of CRC Models- It is hard to get users together.
- It is threatening to some developers.
- Sometimes CRC cards are limited.
Write a short note on relation between sequence diagrams and use case diagram.
Relation between Sequence Diagrams and Use Case Diagram:- Use case diagrams show business use cases, actors and the relationships between them. The relationships between actors and business use cases, state than an actor can use a certain functionality of the business system.
- A sequence diagram can map a scenario described by a use case in step by step detail to define how objects collaborate to achieve your application's goals.
- A Use-Case model is built and the actors are connected to use cases. Each use case represents a task in which the actor participates.
- For each use case, a sequence diagram is built. Each sequence diagram specifies the main interaction steps to be achieved for each use case.
- Some of the interaction steps in a sequence diagram can be deployed in another sequence diagram.
- From the sequence diagrams, use-case relationships are identified.
- Sequence subdiagrams are identified with new use cases, then the inclusion relationships are identified between the use cases specified and the new use cases.
- The sequence diagrams are refined. From the refined sequence diagrams, new use-case relationships are discovered.
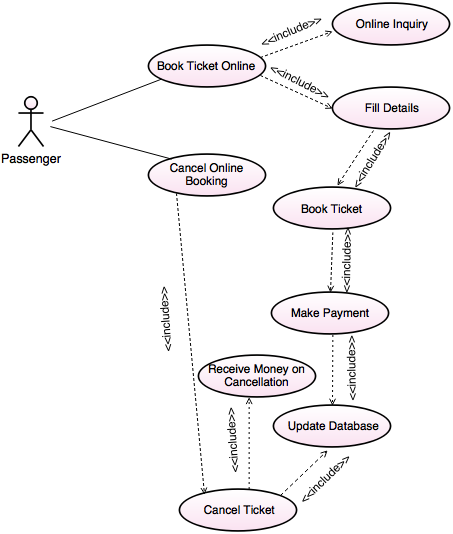
Draw use case diagram for Online Railway Reservation System. Make necessary assumptions.
Use case diagram for Online Railway Reservation System:
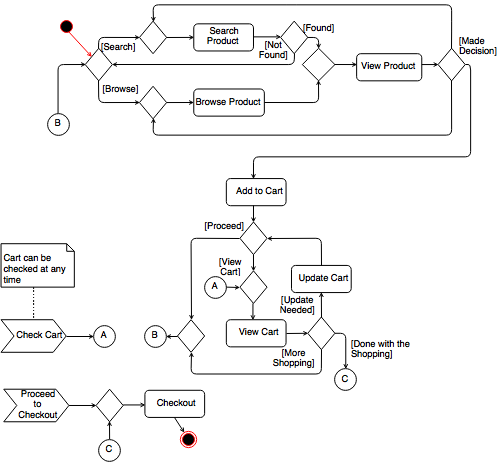
Draw activity diagram for Online Transaction Management System (e-shopping). Make suitable assumptions.