Data Controls
As mentioned previously, one of the important goals of ASP.NET
2.0 is 70% code reduction. The data controls supplied with ASP.NET
2.0 play an important role in making this ambitious goal a reality.
Data source controls provide a consistent and extensible method for
declaratively accessing data from web pages. Data source controls
supplied with ASP.NET 2.0 are as follows:
- <asp:SqlDataSource>: This data
source control is designed to work with SQL Server, OLE DB, Open
DataBase Connectivity (ODBC), and Oracle databases. Using this
control, you can also select, update, delete, and insert data
using SQL commands.
- <asp:ObjectDataSource>: N-tier
methodology allows you to create web applications that are not
only scalable but also easier to maintain. N-tier principle also
enables clean separation, thereby allowing you to easily add new
functionalities. In an n-tier application, the middle-tier objects
may return complex objects that you have to process in your
ASP.NET presentation layer. Keeping this requirement in mind,
Microsoft has created this new control that allows you to
seamlessly integrate the data returned from the middle-layer
objects with the ASP.NET presentation layer.
- <asp:AccessDataSource>: This is
very similar to the SqlDataSource control, except for the
difference that it is designed to work with Access databases.
- <asp:XmlDataSource>: Allows you to
bind to XML data, which can come from a variety of sources, such
as an external XML file, a DataSet object, and so on. Once the XML
data is bound to the XmlDataSource control, this control can then
act as a source of data for data-bound controls such as TreeView
and Menu.
- <asp:SiteMapDataSource>: Provides a site navigation
framework that makes the creation of a site navigation system a
breezy experience. Accomplishing this requires the use of a new
XML file named web.sitemap that lays out the pages of the site in
a hierarchical XML structure. Once you have the site hierarchy in
the web.sitemap file, you can then data-bind the SiteMap
DataSource control with the web.sitemap file. Then the contents of
the SiteMapDataSource control can be bound to data-aware controls
such as TreeView, Menu, and so on.
Now that you have had a look at the data source controls supplied
with ASP.NET 2.0, this section will examine the data-bound controls
that you will normally use to display data that is contained in the
data source controls. These data-bound controls bind data
automatically.
The DataGrid is one of the most popular data-bound controls in
ASP.NET, but in some ways it is a victim of its own success: It is
so rich in functionality that it leaves ASP.NET developers wanting
even more. The DataGrid control does not change much in ASP.NET 2.0,
but the new GridView control offers features commonly requested in
DataGrid and adds a few surprises of its own. In addition, new
controls named DetailsView and FormView simplify the building of
master-detail views and web-editable user interfaces. The new
data-bound controls introduced in ASP .NET 2.0 are:
- <asp:GridView>: This control is the
successor to the DataGrid control that was part of ASP.NET 1.x,
and is used to display multiple records in a web page. However,
the GridView also enables you to add, update, and delete a record
in a database without writing a single line of code. Similarly to
the DataGrid control, in a GridView control each column represents
a field, while each row represents a record. As you would expect,
you can bind a GridView control to a SqlDataSource control, as
well as to any data source control as long as that control
implements the System.Collections.IEnumerable interface.
- <asp:DetailsView>: Can be used in
conjunction with the GridView control to display a specific record
in the data source.
- <asp:FormView>: Provides a user
interface to display and modify the data stored in a database. The
FormView control provides different templates, such as
ItemTemplate and EditItemTemplate, that you can use to view and
modify the database records.
- <asp:TreeView>: Provides a seamless
way to consume information from hierarchical data sources, such as
an XML file, and then display that information. You can use the
TreeView control to display information from a wide variety of
data sources, such as an XML file, a sitemap file, a string, or a
database.
- <asp:Menu>: Like the TreeView control, the Menu control
can be used to display hierarchical data. You can use the Menu
control to display static data, sitemap data, and database data.
The main difference between the two controls is their
appearance.
Listing 1-2 shows you an example of how to use the combination of
SqlDataSource and GridView controls to retrieve and display data
from the ProductCategory table in the AdventureWorks database
without even having a single line of code.
Listing 1-2: Using the SqlDataSource Control to Retrieve
Categories Information
<%@ page language=”C#” %>
<html>
<head
id=”Head1” runat=”server”>
<title>Data Binding using
SqlDataSource
control</title>
</head>
<body>
<form
id=”Form1” runat=”server”>
<asp:SqlDataSource
id=”categorySource”
runat=”server”
ConnectionString=”server=localhost;database=AdventureWorks;uid=user;pwd=word”
SelectCommand=”SELECT * From
Production.ProductCategory”>
</asp:SqlDataSource>
<asp:GridView
DataSourceID=”categorySource” runat=”server”
id=”gridCategories”>
</asp:GridView>
</form>
</body>
</html>
The code declares a SqlDataSource control and a GridView control.
The SqlDataSource control declaration also specifies the connection
string and the SQL statement to be executed as attributes. The
DataSourceID attribute in the GridView is the one that links the
SqlDataSource control to the GridView control. That’s all there is
to retrieving the data from the database and displaying it in a web
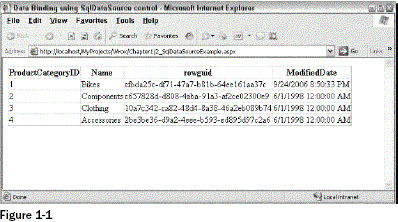
page. Figure 1-1 shows the output produced by the page when
requested from the browser.
More Related links
The
DataList control like the Repeater control is a template driven,
light weight control, and acts as a container of repeated data
items. The templates in this control are used to define the data
that it will contain. It is flexible in the sense that you can
easily customize the display of one or more records that are
displayed in the control...........
This articles describes the ways to preserve page data between
the requests in ASP.NET using Application and Session state
variables.
Article on ASP.NET Server Control Events.
This includes explanation of code security, Principal object,
declarative and imperative security, role-based security, code
access security and code group.
This includes caching mechanism in ASP.NET, its advantages and
types.
This is complete article on ADO.NET with code and interview
questions
AppSetting section is used to set the user defined values. For
e.g.: The ConnectionString which is used through out the project for
database connection.........
Following are the major differences between Server.Transfer and
response.Redirect.....
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a
user.......
|