Write a short note on applications of m-commerce
What is m-commerce?- M-commerce is nothing but the mobile commerce.
- Mobile commerce is commercial transaction conducted electronically through mobile phone and other handheld device.
- M-commerce is also defined as buying and selling of products and services through wireless handheld devices such as mobile phone and personal digital assistants (PDAs).
- It is also known as next-generation e-commerce, m-commerce provides an Internet access without needing to find a place to plug in.
- Mobile commerce makes our life easier and fast.
Applications of m-commerce :
Mobile Banking:
Banks and other financial institutions are offering the use of mobile commerce not only to access account information, but also to transact, e.g. purchasing stocks, remitting money through mobile phones or other handheld device.
Mobile ticketing:
With the help of mobile and other handheld devices customer can book or cancel the tickets. Any type of ticketing can be done through mobile.
Mobile billing:
All types of bill payments and account reviews can be conducted through mobile.
Mobile purchase:
Mobile purchase allows users to shop online at any time and location. Customers can browse and order products by using an inexpensive and secure payment method.
Information services:
A variety of information services can be delivered through mobile which may include financial news, stock data, sports news, traffic data and information etc.
Mobile marketing and advertising:
Using m-commerce the entrepreneur can advertise and market their product. Amazon, flipkart and number of sites advertise and sell the products, all these sites are accessible on mobile.
Mobile brokerage:
Brokerage services, in which stock quotes can be displayed and trading is conducted through the mobile.
What is E-commerce? Discuss its advantages and disadvantages.
What is E-commerce?- E-Commerce deals with buying and selling of products, information, and services over Internet.
- It can also be defined as a use of computing and communication technologies in financial business, online airline reservation, order processing, inventory management etc.
- The major types of E-Commerce are:
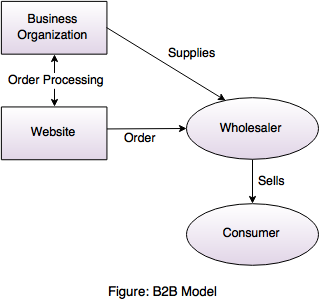
1. B2B (Business-to-Business)- The two business interchange information electronically. The transactions between two businesses are undertaken via intranet and extranet.
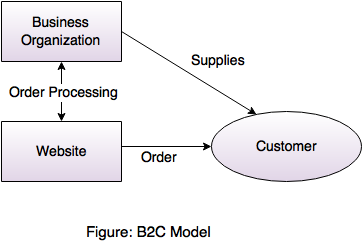
2. B2C (Business-to-Customer)- In this type, business sells product or service directly to consumers over the Internet.
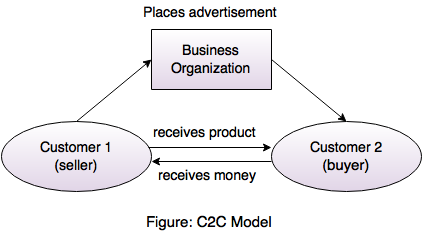
3. C2B (Customer-to-Business)- In this type, consumers sell product or service to business over the Internet.
4. C2C (Customer-to-Customer)- Customer-to-customer electronic commerce involves consumers selling products or services to other consumer. Ex. Ebay, OLX, MagicBricks.
Advantages of E-commerce- It provides 24/7 Hour service to the consumer.
- Consumers have a much wider choice available on online stores.
- It takes Low cost for advertising the products.
- It is easy to create and maintain customer or client .
- It saves time required for shopping and reduces unwanted expenses like traveling.
- E-Commerce reduces the unwanted paper work.
- Easy to start and manage a business.
- In E-Commerce there is no need of physical company set-ups.
- Customers can easily select the product from different provider without moving around physically.
- Consumers can compare product, feature, price and even look up for reviews before purchasing the product.
- It takes Low operational costs and provides better quality of service.
Disadvantages of E-commerce- There is no guarantee of product quality.
- It may take time for the delivery of products .
- Users can not touch or feel the products during online shopping.
- There can be lack of system security and reliability.
- Mechanical failures can cause unpredictable effect on the total process.
- Internet is expensive but still e-commerce cannot be accessed without it.
- Any good or bad person can easily start a business and there are a number of bad sites which only stand for customer's money.
Write a short note on E-commerce models:
- E-commerce is commonly known as electronic marketing.
- It deals with buying and selling of products, information, and services over Internet.
- It can also be defined as a use of computing and communication technologies in financial business, online airline reservation, order processing, inventory management etc.
- E-commerce refers to Internet market which includes manufacturing, development, marketing, sales and support, etc.
The major types of E-Commerce model are:
1. B2B (Business-to-Business)- The two businesses exchange information electronically. The transactions between two businesses are undertaken via intranet and extranet.
- In this model both the parties are business holders there is no involvement of the customer.
- B2B includes online transaction between organization and their partners.
- The B2B market consist of two components: e-infrastructure and e-market.
- E-infrastructure is nothing but the architecture of B2B market.
- E-infrastructure is defined as a combination and interworking of hardware, software, resources (data, digital libraries), communications (protocols, access rights and networks), the people and organizational structures.
- E-markets are the web sites where buyer and seller can interact with each other and conduct transaction.
- The most common examples of B2B are IBM, Cisco, Intel, Dell etc.
- Example: Intel selling microprocessor to Dell.
 2. B2C (Business-to-Customer)
2. B2C (Business-to-Customer)- Business-to-Customer is the most common type of business model, In which, business sells product or service directly to consumers over the Internet.
- Most common uses of B2C e-commerce model are in the areas of purchasing products and information, personal banking, etc.
- A customer can see products shown on the website of business organization.
- Consumers can compare product, feature, price and even look up for reviews before purchasing the product.
- Customers can easily select the product from different provider without moving around physically.
- The most common examples of B2C e-commerce are Amazon, flipkart, Nike, Dell, etc.
 3. C2B (Customer-to-Business)
3. C2B (Customer-to-Business)- In this type, consumers sell product or service to business over the Internet.
- C2B model is also called as reverse auction model.
- In this model, customers can sell the product and service to the company and company pay the customers.
- This model is completely reversal to the traditional business model in which business sells products and services to the customer.
4. C2C (Customer-to-Customer)- Customer-to-customer electronic commerce involves consumer selling product or service to other consumer.
- In a consumer-to-consumer (C2C) model, the website provides the facility of transaction between two consumers.
- Website which follows C2C e-commerce model helps customer to sell their assets like residential property, cars, motorcycles etc. or rent a room by publishing their information on the website.
- Most of the sites does not charge for its service.
- Auction sites such as eBay, OLX, quickr are the most common examples of C2C ecommerce sites.
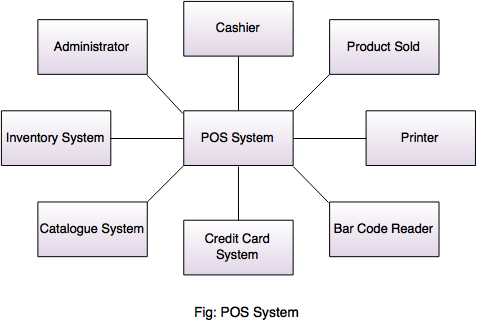
Write a short note on POS:
- POS is an abbreviation for Point-of-Sale.
- The place where sales are made. A good example of POS can be a supermarket (e.g. D mart) or department store (e.g. Central).
- The POS system is able to record and track customer orders, process credit and debit cards, connect to other systems in a network, and manage inventory.
- Point of Sale (POS) Hardware & Software includes : electronic cash register systems, touch-screen display, barcode scanners, receipt printers, scales and pole displays.
- Point of Sale Systems are used in many different industries, ranging from restaurant, hotel & hospitality, beauty parlor, casino, stadium, and the retail environment.
- Generally, POS system contain a personal computer, which is called as POS Terminal.
- POS terminal is provided with application-specific programs and I/O devices for the particular environment in which it will serve.
- A POS system for a medical store, for example, is likely to have all medicine names stored in a database that can be queried for information in a number of ways.
Figure shows the architecture of POS system.
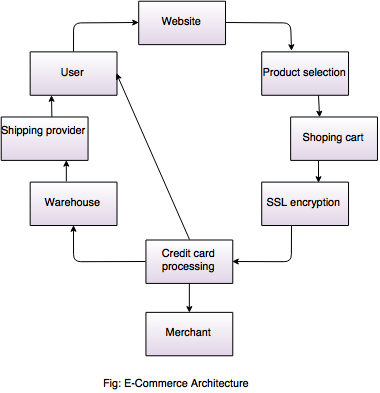
Explain E - commerece architecture.
- E-commerce is commonly known as electronic marketing.
- E-Commerce deals with buying and selling of products, information, and services over Internet.
- Under e-commerce scenario, general flow of most of the business activities is:
1. First of all buyer visits the seller's site.
2. If required then buyer has to go through the registration.
3. All these details are stored in database at server side.
4. If required then buyer enters his/her login name and password.
5. Then server verify the login name and password.
6. Buyer pass through the product catalog and select required items.
7. Buyer add this selected items to the shopping cart.
8. After confirmation from the buyer, system asks for the contact number and e-mail id of the buyer for the delivery.
9. Then system asks buyer to pay by using the provided payment option.
10. If payment is electronic then buyer enter the required details for payment. All details are verified and transaction ends after payment.
Figure shows the architecture of e-commerce.
 What e-commerce requires:
Internet:
What e-commerce requires:
Internet:- Internet is necessary for communication between buyer and seller. If there is no Internet, then there is no communication between buyer and seller electronically.
Firewall:- It is used to provide reasonable protection against hackers, network intruders, etc. Hackers are the people who wish to harm organization's system, who wish to know personal and financial details of customer.
Seller:- Seller is an organization or a person who wish to sell products and services over Internet. Web sites are used for representing the seller on the Internet. These web sites are created for selling or buying products and services. It includes all the functionalities which are required for business transaction, like registration, catalog, payment processing, etc.
Buyer:- Buyer is an organization or a person who wish to buy products and services over Internet.Payment Processor: Entire world is the market for e-commerce, which means doing business internationally. International business means handling multiple languages, multiple currencies, different tax laws, and different shipping customer rules. For this task e-commerce must have some mechanism that can process electronic payments in a secured way with all diversities.
Data Storage:- Data about sell, purchase, products, services, payments, delivery and business is stored in database. Generally data warehouse or database is used by organization for storing data.
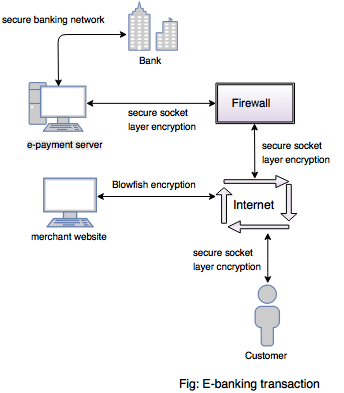
Explain various electronic payment methods. How transactions are performed in E-banking.
- Internet payment system is a mechanism which is used to transfer fund from customer to merchant or business to business through the Internet.
- Electronic payment has completely changed the business processing by reducing paper work, transaction costs, labour cost.
- There are many payment options available, including
1. Credit card payment
2. Debit card payment
3. E-Cheque
4. Electronic funds transfer
Credit card payment- Credit cards are a safe, secure, and commonly used remote payment system.
- Credit card is small plastic card with a magnetic stripe which has number and code on it.
- It has some fixed amount to spend.
- Customer has to repay the spend amount after a certain time period.
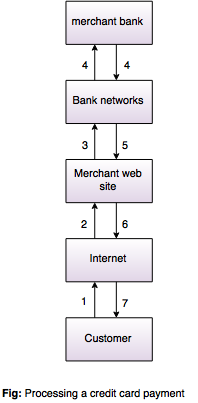
- Entities involved in a credit card system are:
Card holder: Card holder is an authorized person (customer) who holds credit card which has been issued from an issuer.
Merchant: A person or an organization that wish to sell product and services to the customer.
Issuer: An issuer is a bank that issues card to the card holder.
Acquirer:An acquirer is a bank that act as an agent which has relationship with merchant and issuer.
Given diagram shows processing of credit card system:
 Debit card payment
Debit card payment- Debit Card is the second largest e-commerce payment method in India.
- It is compulsory to have a bank account before getting a debit card from the bank.
- With the debit card, customer can only pay for purchased goods with the money that already exists in customers accounts as opposite to the credit card where the amounts that the buyer spends are collected and have to be paid for as a bill at the end of the billing period.
- Debit cards use credit card payment processing technology to access funds directly from the card holder’s transaction account.
E-Cheque- Cheques and money orders are rare payment methods for online transactions because of the time taken to send, receive and process the payment
- An e-cheque is an electronic fund transfer method which can withdraw money directly from bank account.
- E-cheque is like writing a cheque, only it is done electronically.
- Bank account holder can make payment online without using credit card.
- After registration a buyer can contact sellers of products and services.
- The buyer sends a cheque to the seller for a certain amount of money.
- The cheque can be send using email or another transport method.
- After depositing the cheque it helps in authorizing the transfer of balance from the account against which the cheque was drawn to the account where the cheque is deposited.
- Electronic cheque are casted in the same as paper cheque but are initiated electronically.
- Digital signature are used for signing & endorsing which require digital certificates to authenticate the payer, his bank & account.
- Cheques are delivered by direct transmission like telephone lines or by public networks such as the Internet.
Electronic funds transfer (EFT)- This method involves direct transfer of fund from buyer's to seller's account.
- EFT is a very popular electronic payment method to transfer money from one bank account to another bank account.
- This transaction can be done by using computer or ATM .
- Customer logins to the bank's website and registers another bank account.
- Customer places a request to transfer certain amount to that account.
- Customer's bank transfers amount to other account if both accounts are in same bank, otherwise transfer request is forwarded to ACH (Automated Clearing House) to transfer amount to other account and amount is deducted from customer's account.
- Once amount is transferred to other account, customer gets acknowledged by the bank.
Figure shows how transaction is performed in E-banking: