▼ Meet the world's first robot table tennis tutor, FORPHEUS! [02-28-17]
 The world’s first robot table tennis tutor named FORPHEUS in Japan has set a new Guinness World Record for its unique ability of being able to play the game better than most humans. The world’s first robot table tennis tutor named FORPHEUS in Japan has set a new Guinness World Record for its unique ability of being able to play the game better than most humans.
It has been given the Guinness title for its advanced technological intelligence and educational capabilities.
FORPHEUS is for Future Omron Robotics Technology for Exploring Possibility of Harmonised aUtomation with Sinic Theoretics.
Its goal is to harmonise humans and robots, by way of teaching the game of table tennis to human players.
It has cutting-edge vision and motion sensors which it uses to gauge movement during a match.
|
▼ SAP SE, Apple develop new software tool [02-28-17]
 Apple Inc and German software maker SAP SE has launched a tool for helping developers build iPhone apps for big businesses. Apple Inc and German software maker SAP SE has launched a tool for helping developers build iPhone apps for big businesses.
The software tool is set for release on March 30 and is designed to permit developers to easily feed data between SAP's business linked software system and Apple's customer centric iOS mobile platform.
Most of the SAP systems are used on personal computers rather than mobile devices. SAP will change this by working with Apple to make software tools that can access its systems from apps on iPhone or iPad.
The tool can let employees log into business applications with fingerprint readers on iPhones rather than passwords. This could also replace bulky inventory scanning gun used in warehouses with iPhones.
With the iPhone sales diminishing in numbers, Apple has launched partnerships with IBM, Cisco and Deloitte & Touche LLP to help businesses access iOS apps.
SAP partnership also gives iOS developers a way to gain revenue in an era where the App Store's growth is driven by downloads in China and by game makers.
Apple in 2017 said that developers made an amount of USD 20 billion from the app store in 2016, marking an increase of 40% since 2015.
Business apps could help Apple compete efficiently against Microsoft Corp whose window software dominates in the corporate world.
SAP SE: Know More
- CEO: Bill McDermott (since 21 May 2014)
- Headquarters: Walldorf, Germany
- Revenue: 22.06 billion EUR (2016)
- Subsidiaries: Hybris, SuccessFactors, Fieldglass, SAP Ariba, etc
|
▼ ZTE announces 5G smartphone Gigabit [02-28-17]
 ZTE announced the launch of Gigabit - the world’s first 5G-ready smartphone at a MWC event on 26th February. ZTE announced the launch of Gigabit - the world’s first 5G-ready smartphone at a MWC event on 26th February.
The company says the smartphone is capable of download speeds reaching up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps).
With the new device, the way people stay connected will be changed forever.
Focusing on 5G technologies will be one of the key priorities of ZTE's global development.
The device is powered by Snapdragon 835’s advanced X16 LTE modem along with 4x4 MIMO antenna technology and 256-QM modulation.
The device will reportedly allow users to experience 360-degree panoramic Virtual Reality video and fast downloads of ultra Hi-Fi audio and videos.
As expected, ZTE has launched its Gigabit smartphone at the MWC event.
It is the first one to come with Qualcomm's top-end Snapdragon 835 chipset that is being produced by Samsung.
ZTE Gigabit is also the first in the world to have a consumer-ready 5G technology to attain gigabit speeds on a supported cellular network.
The phone utilizes Snapdragon 835's advanced X16 LTE modem along with 4x4 MIMO antenna technology and 256-QM modulation to achieve speeds even available on most routers for home-use.
Intel chips deploying its XMM 7560 modem and Samsung's Exynos Series 9 chipset also support gigabit LTE speeds.
The latest network technology currently being developed and tested is over the 4G LTE, but not exactly 5G or fifth generation of network.
Though many OEMs have started to work on 5G-capable devices, which will offer faster-than-Wi-Fi connectivity speeds enabling to download full movies within seconds.
Faster LTE networks work through their testing phase and are not launched anywhere. The 5G standardization and application of key 5G technologies to the existing network and will establish collaborations with leading chip makers and Tier 1 operators to develop 5G network architecture.
The one ZTE demonstrated at the MWC booth is its self-developed Pre5G Giga+ Mobile Broadband (MBB) solution.
The connectivity speeds demonstrated on the device are about three times faster than 4G LTE smartphones, allowing streaming of 360-degree VR and instant cloud storage.
ZTE: Know More
- ZTE Corporation, commonly shortened to ZTE, is a Chinese multinational telecommunications equipment and systems company.
- It is headquartered in Shenzhen, Guangdong.
- ZTE operates in three business units: carrier networks, terminals and telecommunication. Wikipedia
- Headquarters: Shenzhen, China
- Revenue: 81.47 billion CNY (2014)
- Founded: 1985, Shenzhen, China
|
▼ NASA's Solar Probe Plus to reach the sun [02-28-17]
 NASA aims to send its first robotic spacecraft to the Sun in 2018 and is slated to get within 6 million kms of the blazing star to probe the atmosphere. NASA aims to send its first robotic spacecraft to the Sun in 2018 and is slated to get within 6 million kms of the blazing star to probe the atmosphere.
Humans have sent spacecrafts to Mars, moon and interstellar space. NASA will now launch Solar Probe Plus mission to the Sun.
The sun is about 149 million km from earth.
Mission will unveil why the surface of the Sun called the photosphere is not as hot as the atmosphere called the corona.
NASA has indicated that the sizzling temperature of the Sun's atmosphere above is a sizzling 2 million degrees Celsius.
The surface temperature of the Sun is only around 5,500 degree celsius.
As you move away from the centre to the atmosphere, it is hotter which is one of the puzzles of the sun.
Scientists also want to know how solar winds get speed. The Sun blows a stream of charged particles in all directions at a million miles an hour. But scientists do not understand how that gets accelerated.
The mission may also ascertain why the Sun occasionally emits high-energy particles that are a danger to unprotected astronauts and spacecraft.
NASA has designed an 11.4 centimetres carbon-composite shield, which is designed to withstand temperatures outside the spacecraft of 1,370 degrees Celsius.
The unmanned probe will have special heat tubes called thermal radiators that will radiate heat that permeates the heat shield to open space, so it does not go to the instruments, which are sensitive to heat.
Sun: Know More
- Distance to Earth: 149.6 million km
- Surface temperature: 5,778 K
- Radius: 695,700 km
- Mass: 1.989 × 10^30 kg
- Orbits: Galactic Centre
- Spectral type: G2V
|
▼ e-waste can generate electricity : IIT Madras scientists [02-27-17]
 Scientists at IIT, Madras have come up with a novel technique where e-waste can be used as a resource not only to treat waste water. Scientists at IIT, Madras have come up with a novel technique where e-waste can be used as a resource not only to treat waste water.
It can also be used to generate electricity simultaneously, making it an important innovation to deal with fast growing menace of such hazardous waste in the country.
Under this technique, scientists use e-waste component like "LED\LCD (liquid crystal coated polaroid) glass" as an electrode material in 'Microbial Fuel Cells' (MFCs).
This is primarily a technology used for only waste water treatment.
Use of e-waste as an electrode, however, helps it to generate electricity and recover metals for reuse.
Use of waste to study waste and generate electricity is a novel concept.
Technologies available in the country at present are generally meant for only recovering and recycling components like glass, plastic, printed circuit board, hard drives, batteries and valuable metals.
But this new technology, the scientists claim, can use LED\LCD glass component of e-waste for the twin jobs–waste water treatment and electricity production.
IIT Madras: Know More
- Director: Bhaskar Ramamurthy
- Founded: 1959
- Chairperson: Pawan Kumar Goenka
- Motto: Sanskrit:सिद्धिर्भवति कर्मजा/ (English:Siddhirbhavati Karmaja)
|
▼ AAI, IATA launch e-billing solution SKYREV360 [02-27-17]
The state-owned Airport Authority of India (AAI) along with International Air Transport Association (IATA) launched SKYREV360, an e-billing solution for airport operators across the world.
SKYREV360 will aid airport operators and air navigation services providers worldwide to overcome the issues of revenue leakages, besides reducing redundancies.
It will also help in the reduction in disputes, easy integration with all external systems and curtailing the debt collection period to the minimum.
It has been developed for the electronic billing solution for data, e-invoicing and collection of tariff from the airlines.
It is being used by the AAI for several years now.
IATA: Know More - Headquarters: Montreal, Canada
- CEO: Tony Tyler (since 1 Jul 2011)
- Founded: 19 April 1945, Havana, Cuba
- Type of business: International trade association
|
▼ Perspective : New technology by Google Alphabet Inc and Jigsaw to track abuse [02-24-17]
 Alphabet Inc's Google and subsidiary Jigsaw launched on 23rd Feb 2017 a new technology to help news organisations and online platforms identify abusive comments on their websites. Alphabet Inc's Google and subsidiary Jigsaw launched on 23rd Feb 2017 a new technology to help news organisations and online platforms identify abusive comments on their websites.
The technology, called Perspective, will review comments and score them based on how similar they are to comments people said were toxic or likely to make them leave a conversation.
The tool has been tested on New York Times and the companies hope to extend it to other news organisations such as The Guardian and The Economist as well as websites.
Perspective examined hundreds of thousands of comments that had been labelled as offensive by human reviewers to learn how to spot potentially abusive language.
The company was open to rolling out the technology to all platforms, including larger ones such as Facebook and Twitter where trolling can be a major headache.
The technology could in the future be expanded to trying to identify personal attacks or off-topic comments too.
Perspective will not decide what to do with comments it finds are potentially abusive; rather publishers will be able to flag them to their moderators or develop tools to help commenters understand the impact of what they are writing.
The initiative against trolls follows efforts by Google and Facebook to combat fake news stories in France, Germany and the United States after they came under fire during the US presidential vote.
The debate surrounding fake news has led to calls from politicians for social networks to be held more liable for the content posted on their platforms.
Jigsaw: Know More
- Formerly called: Google Ideas (2010–2015)
- Type: Think tank
- Founded: 2010
- Founders: Eric Schmidt
- Headquarters: New York City, United States
- Jared Cohen (President)
- Parent : Google (2010–2015)/Alphabet Inc. (2015–present)
- Website: jigsaw.google.com
|
▼ Earth like planet trappist-1 [02-24-17]
 For the first time, astronomers have discovered seven Earth-size planets orbiting a single nearby star - and these new worlds could hold life. For the first time, astronomers have discovered seven Earth-size planets orbiting a single nearby star - and these new worlds could hold life.
This cluster of planets is less than 40 light-years away in the constellation Aquarius, according to NASA and the Belgian-led research team who announced the discovery Wednesday.
The planets circle tightly around a dim dwarf star called Trappist-1, barely the size of Jupiter.
Three are in the so-called habitable zone, the area around a star where water and, possibly life, might exist.
Scientists said they need to study the atmospheres before determining whether these rocky, terrestrial planets could support some sort of life.
But it already shows just how many Earth-size planets could be out there - especially in a star ripe for extraterrestrial life.
The more planets like this, the greater the potential of finding one that's truly habitable. Until now, only two or three Earth-size planets had been spotted around a star.
The potential for more Earth-size planets in the Milky Way galaxy is mind-boggling.
The discovery gives us a hint that finding a second Earth is not just a matter of if, but when.
University of Liege's Michael Gillon and his team reported finding three planets around Trappist-1. Now the count is up to seven, and scientists said there could be more.
This crowded yet compact solar system - 235 trillion miles away - is reminiscent of Jupiter and its Galilean moons, according to the researchers.
Altogether, astronomers have confirmed close to 3,600 planets outside our solar system since the 1990s, but barely four dozen are in the potential habitable zone of their stars.
Of those, just 18 are approximately the size of Earth.
Both ground and space telescopes were used to identify and track the seven Trappist-1 planets, which they label simply by lowercase letters, "b" through "h."
As is typical in these cases, the letter "A" - in upper case - is reserved for the star.
Planets cast shadows on their star as they pass in front of it; that's how the scientists spotted them.
Tiny, cold stars like Trappist-1 were long shunned by exoplanet-hunters (exoplanets are those outside our solar system).
But the astronomers decided to seek them out, building a telescope in Chile to observe 60 of the closest ultracool dwarf stars.
Their Trappist telescope lent its name to this star.
While faint, the Trappist-1 star is close by cosmic standards, allowing astronomers to study the atmospheres of its seven temperate planets.
All seven look to be solid like Earth - mostly rocky and possibly icy, too.
They all appear to be tidally locked, which means the same side continually faces the star, just like the same side of our moon always faces us.
Life could still exist at these places, the researchers explained.
Chemical analyses should indicate life with perhaps 99 percent confidence.
|
▼ Cyber Swachhta Kendra launched by CERT-In [02-24-17]
 At a time when cyber attacks are increasing, the government through its Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-in) on 21st Feb 2017 launched Cyber Swachhta Kendra. At a time when cyber attacks are increasing, the government through its Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-in) on 21st Feb 2017 launched Cyber Swachhta Kendra.
This a new desktop and mobile security solution for a secure cyber space in the country.
The new solution will notify, enable cleaning and secure systems of end-users to prevent further infections.
Around 13 banks and internet service providers using this facility.
Cyber Swachhta Kendra will also enhance awareness among citizens regarding botnet and malware infection along with measures to be taken to secure their devices.
National Cyber Coordination Centre will be operational by June 2017. The government also announced it would set up CERT-Ins at the state level as well.
The government will set up 10 more STQC (Standardisation Testing and Quality Certification) testing Facilities.
Testing fee for any start-up that comes up with a digital technology in the quest of cyber security will be reduced by 50 per cent.
Part of the solution, USB Pratirodh is a desktop security solution that controls the usage of removable storage media like pen drives, external hard drives and other USB-supported mass storage devices.
M-Kavach tool offers a comprehensive mobile device security solution for Android devices addressing threats related to mobile phones.
AppSamvid is a desktop solution which protects systems by allowing installation of genuine applications through white listing. This helps in preventing threats from malicious applications.
CERT-in: Know More
- CERT-In (the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team) is a government-controlled information technology (IT) security organization.
- The purpose of CERT-In is to respond to computer security incidents.
- It also issues report on vulnerabilities and promote effective IT security practices throughout the country.
- CERT-In was created by the Indian Department of Information Technology in 2004.
- CERT organizations throughout the world are independent entities, although there may be coordinated activities among groups.
- The first CERT group was formed in the United States at Carnegie Mellon University.
|
▼ NASA scientists find microorganisms 60,000 years old! [02-24-17]
 Scientists from NASA’s Astrobiology Institute have discovered living microorganisms (most of them bacteria) trapped inside crystals for as long as 60,000 years. Scientists from NASA’s Astrobiology Institute have discovered living microorganisms (most of them bacteria) trapped inside crystals for as long as 60,000 years.
These were found in a Naica mine in Mexico.
These ancient microbes have evolved so they can survive on a diet of sulphite, manganese and copper oxide.
The discovery has caused concern for astrobiologists about bringing back samples collected on space missions in the solar system as dangerous extraterrestrial organisms could accidentally enter into Earth on a returning spaceship.
Besides there is also risk that Earth organisms could contaminate other planets in the course of missions.
Bacteria: Know More
- Bacteria constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms.
- Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals.
- Scientific name: Bacteria
- Rank: Domain
|
▼ CBEC launches GST mobile app [02-24-17]
 In step with the Government’s Digital India initiative, the Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) has launched a mobile application for Goods and Services Tax. In step with the Government’s Digital India initiative, the Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) has launched a mobile application for Goods and Services Tax.
Taxpayers can readily access a host of GST information such as:
- Migration to GST-Approach and guidelines for migration
- Draft Law-Model GST Law, IGST Law and GST Compensation Law
- Draft Rules-Rules related to Registration, Returns, Payment, Refund and Invoice
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on GST
- Various resources on GST such a videos, articles etc.
- Related Website Links
- Helpdesk/Email Contact
The Mobile Application enables taxpayers to be well informed of the latest updates on GST. Taxpayers can also provide feedback and contact CBEC’s 24x7 helpdesk “CBEC Mitra” through a toll-free number or email, at the flick of a button. The mobile application can be downloaded free of cost on Android platforms. The iOS version will be made available shortly. GST Mobile Application is a yet another initiative by CBEC towards improving ease of doing business and providing outstanding taxpayer services.
|
▼ Most distant pulsar in the universe located [02-23-17]
 The pulsar is 50 million light years away. The pulsar is 50 million light years away.
It's a collapsed star spinning around at an increasing speed and sending out as much energy in one second as the Sun does in 3.5 years.
The discovery was made by scientists using the x-ray observatory space craft XMM-Newton managed by the European Space Agency (ESA).
The newly found pulsar is a 1000 times brighter than previously thought possible and also the most distant of its kind ever detected.
It completes one rotation in just over a second.
The discovery of this very unusual object, by far the most extreme ever discovered in terms of distance, luminosity and rate of increase of its rotation frequency, sets a new record for XMM-Newton, and is changing our ideas of how such objects really function.
XMM-Newton observed the object several times in the last 13 years, with the discovery a result of a systematic search for pulsars in the data archive–its 1.13 s periodic pulses giving it away.
The signal was also identified in NASA's Nustar archive data, providing additional information.
Previously, it was held only black holes at least 10 times more massive than our sun feeding off their stellar companions could achieve such extraordinary luminosities, but the rapid and regular pulsations of this source are the fingerprints of neutron stars and clearly distinguish them from black holes, according to scientists.
Only a neutron star is compact enough to keep itself together while rotating so fast.
The scientists think there must be a strong, complex magnetic field close to its surface, such that accretion onto the neutron star surface is still possible while still generating the high luminosity.
What are Pulsars?
- Pulsars are spinning, magnetised neutron stars that sweep regular pulses of radiation in two symmetrical beams across the cosmos.
- If suitably aligned with Earth these beams are like a lighthouse beacon appearing to flash on and off as it rotates.
- They were once massive stars that exploded as a powerful supernova at the end of their natural life. They small and extraordinarily dense stellar corpses.
|
▼ World's smallest frog discovered! [02-22-17]
 Professor SD Biju from Delhi University (DU) and his team discovered four new miniature species. Professor SD Biju from Delhi University (DU) and his team discovered four new miniature species.
This is now listed among the smallest known frogs in the world.
The scientists were surprised by the relative abundance of these new miniature species.
In all Biju's team have discovered seven new frog species belonging to the genus Nyctibatrachus, commonly known as Night Frogs.
This finding is a result of five years of extensive explorations in the Western Ghats global biodiversity hotspot in India.
Four out of seven of the new species are miniature-sized frogs (12.2-15.4 mm), which can sit on a coin or a thumbnail.
These are among the smallest known frogs in the world.
Unlike other frogs in the genus that are predominantly stream dwelling, the new miniature frogs were found under damp forest leaf litter or marsh vegetation.
The newly sampled frogs were confirmed as new species by using an integrated taxonomic approach that included DNA studies, detailed morphological comparisons and bioacoustics.
Earlier Night Frog genus comprised of 28 recognized species of which only three were miniature-sized (<18mm).
Now the total number of known Nyctibatrachus species has increased to 35, of which 20% are diminutive in size.
This frog genus is endemic to the Western Ghats of India and represents an ancient group of frogs that diversified on the Indian landmass approximately 70-80 million years ago.
Among the new species are four true miniatures, between 10 and 15 mm body length, among the smallest of frogs.
These seem to be common locally and they probably were overlooked because of their small size.
They occur more terrestrially, in leaf litter.
However, the future of many of the new species may be bleak. All the newly described species are currently known only from single localities in the southern Western Ghats, and some lie outside protected areas.
Researchers found the Radcliffe's Night frog and the Kadalar Night Frog inside private or state-owned plantation areas facing threats such as habitat disturbance, modification and fragmentation.
The Athirappilly Night Frog was found in close vicinity to the Athirappilly waterfalls and the Sabarimala Night Frog near the Sabarimala pilgrimage centre, both of which are disturbed by anthropogenic activities.
"Over 32%, that is one-third of the Western Ghats frogs are already threatened with extinction.
Western Ghats: Know More
- Elevation: 2,695 m
- Area: 160,000 km²
- Highest point: Anamudi
- Passes: Tamhini Ghat, Naneghat, Palakkad Gap, Kasara ghat
- Types of rock: Basalt, Limestone
|
▼ An attempt to extract uranium from sea water! [02-22-17]
 Scientists are developing a new way of extracting uranium from seawater, an advance that may help countries that lack resources to harness nuclear power from the oceans. Scientists are developing a new way of extracting uranium from seawater, an advance that may help countries that lack resources to harness nuclear power from the oceans.
Researchers have long known that uranium dissolved in seawater combines chemically with oxygen to form uranyl ions with a positive charge.
Extracting these uranyl ions involves dipping plastic fibers containing a compound called amidoxime into seawater. The uranyl ions essentially stick to the amidoxime.
When the strands become saturated, the plastic is chemically treated to free the uranyl, which then has to be refined for use in reactors just like ore from a mine.
How practical this approach is depends on three main variables - how much uranyl sticks to the fibres, how quickly ions can be captured and how many times the fibres can be reused.
Researchers from Stanford University in the US improved on all three variables: capacity, rate and reuse.
Their key advance was to create a conductive hybrid fibre incorporating carbon and amidoxime.
By sending pulses of electricity down the fibre, they altered the properties of the hybrid fibre so that more uranyl ions could be collected.
Researchers supervised lab tests that compared Stanford's amidoxime-carbon hybrid fibres with today's amidoxime fibres.
The extent of uranyl each type of fibre could hold before reaching saturation was tested.
By the time the standard amidoxime fibre had become saturated, Stanford's amidoxime-carbon hybrid fibres had already adsorbed nine times as much uranyl and were still not saturated.
The electrified fibre captured three times as much uranyl during an 11-hour test using seawater from Half Moon Bay, about an hour from Stanford and had three times the useful lifespan of the standard amidoxime.
Trace amounts of uranium exists in seawater, but efforts to extract that critical ingredient for nuclear power have produced insufficient quantities to make it a viable source for those countries that lack uranium mines.
A practical method for extracting that uranium, which produces higher quantities in less time, could help make nuclear power a viable part of the quest for a carbon-free energy future.
Researchers believe that a practical way to extract uranium from seawater is needed to reduce the energy insecurity of nations that depend on nuclear power but lack uranium within their own borders.
Uranium: Know More
- Symbol: U
- Atomic number: 92
- Atomic mass: 238.02891 u ± 0.00003 u
- Electron configuration: [Rn] 5f36d17s2
- Discovered: 1789
- Melting point: 1,132°C
- Discoverer: Martin Heinrich Klaproth
|
▼ ESA to collaborate with ISRO for space missions [02-20-17]
 While the European Space Agency (ESA)'s Gaia satellite mission is on its multi-dimensional space probe, mapping a billion stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, ESA's Senior Scientific Advisor Mark McCaughrean reveals ESA's plan for further collaboration with Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in space missions. While the European Space Agency (ESA)'s Gaia satellite mission is on its multi-dimensional space probe, mapping a billion stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, ESA's Senior Scientific Advisor Mark McCaughrean reveals ESA's plan for further collaboration with Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in space missions.
On ISRO's historic launch of 104 satellites at one go, he says it's the precision in placing satellites and cost reduction.
ESA is planning 15 space missions including Bepe Colombo to Mercury in 2018 and JUICE to Jupiter in 2022.
Earlier, ESA had collaborated with ISRO on Chandrayaan-1 mission to Moon.
In its space mission, ESA has collaborative efforts with 22 countries including the US, Russia, China, India and Japan.
It is expected to increase with the commercial launches.
ON ESA's plan for 15 space missions, the Bepe Colombo will be the first probe to Mercury in 2018.
It is a joint mission between ESA and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the Sun's enormous gravity poses a challenge to place the spacecraft into a stable orbit around Mercury.
Then, the ambitious Jupiter Icy moons Explorer (JUICE) to Jupiter in 2022.
The explorer will spend at least three years making detailed observations of the giant gaseous planet Jupiter and three of its largest moons–Ganymede, Callisto and Europa.
The ice crust is much deeper and there may be forms of life in these moons.
Missions to Neptune and Uranus haven't been planned yet as it would take about 20 to 30 years to reach there, he said.
To probe the possibility of life on other planets, humans have begun space exploration since the first human spaceflight of Russia in 1961 and now plans are afoot by NASA and SpaceX to colonise Mars to help humanity establish a permanent colony in Mars in the next 50 to 100 years.
On ESA's human space flight to Mars, he said it could be after 10 to 20 years. Now it plans robotic exploration to Mars with NASA.
ESA Gaia & Other Missions: Know More
- It ambitious space mission to scan a six-dimensional map of our Milky Way galaxy of about one billion stars, which is about one percent of the Galactic stellar population.
- ESA is also preparing for Euclid mission to observe billions of galaxies, to map and measure dark matter and dark energy which constitutes roughly about 80 percent of the mass of the Universe.
- Studies on dark matter reveal that the universe today is expanding faster than in the past.
- Such expansion is possible only if the universe contained enough energy to overcome gravity.
- ESA has a program to build a gravitational wave detector by 2030, it's the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) mission to observe and measure gravitational waves directly by using laser interferometry.
|
▼ Origami shield to protect law officers from gun fire! [02-20-17]
 Scientists have created an origami-inspired, lightweight bulletproof shield that can protect law enforcement officials from gunfire. Scientists have created an origami-inspired, lightweight bulletproof shield that can protect law enforcement officials from gunfire.
The new barrier can be folded compactly when not in use, making it easier to transport and deploy.
When expanded - which takes only five seconds - it can provide cover for officers and stop bullets from several types of handguns.
Scientists wanted to create something that was compact, portable, lightweight and worked really well to protect law officers.
Working with law enforcement agencies, researchers learned much of what is currently used has not evolved much from medieval times: shields that are mostly flat, awkward plates that cover only one person.
Current barriers are so heavy and cumbersome they make it difficult for officers to move into position.
The barrier researchers designed is made of 12 layers of bulletproof Kevlar and weighs only 24 kg.
The barrier uses a Yoshimura origami crease pattern to expand around an officer, providing protection on the side in addition to protecting them in the front.
In testing, the barrier successfully stopped bullets from 9 mm, 0.357 Magnum and 0.44 Magnum pistols.
A 0.44 Magnum would actually tip it over, but that did not happen.
The barrier is very stable, even with large bullets hitting it.
Since Kevlar fabric is subject to fraying, abrasion and is sensitive to sunlight and water, the team also made a concentrated effort to reinforce it against the environment.
It goes from a very compact state that you can carry around in the trunk of a car to something one can take with them, open up and take cover behind to be safe from bullets.
Then one can easily fold it up and move it if you need to advance your position.
In addition to protecting police officers, researchers believe the barrier could be used to protect children in a school or a wounded person in an emergency situation.
|
▼ Cloud Seeding Programme launched in Solapur [02-20-17]
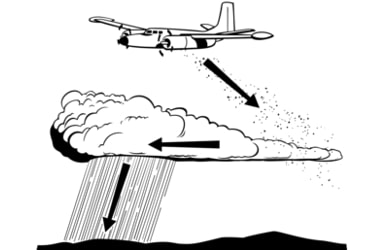 Maharashtra Government approves cloud seeding project for 2017 monsoon Maharashtra Government has approved INR. 250 crore Cloud Seeding Programme during 2017 monsoon season to produce sufficient rain. Maharashtra Government approves cloud seeding project for 2017 monsoon Maharashtra Government has approved INR. 250 crore Cloud Seeding Programme during 2017 monsoon season to produce sufficient rain.
Under this programme, weather scientists using aircrafts will spray chemicals (silver iodide) over clouds hovering above Solapur district, a rain shadow region of Western Ghats in the state.
This will be the first controlled experiment to quantify the extent to which clouds form water drops large enough to make rain.
This programme, coordinated by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, will be the first controlled experiment to quantify the extent to which clouds form water drops large enough to make rain.
In this experiment, scientists will fly two aircraft and spray silver iodide and dry ice on 100 clouds and compare them with 100 unseeded clouds.
Ground radar will be used to track the clouds and verify which ones contributed rain.
Solapur: Know More
- Solapur is a city located in the south-eastern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra.
- Solapur is located on major road and rail routes between Mumbai and Hyderabad.
- Area: 148.9 km²
- Weather: 27°C, Wind N at 2 km/h, 29% Humidity
- Population: 872,478 (2001) (UN)
|
▼ ISRO tests Cryogenic Engine for GSLV Mark 3 successfully [02-20-17]
 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully ground tested India’s largest indigenously developed Cryogenic Upper Stage engine for GSLV Mark III. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully ground tested India’s largest indigenously developed Cryogenic Upper Stage engine for GSLV Mark III.
It was tested for full 10 minutes at ISRO’s Liquid Propulsion Complex (ILPC) at Mahendragiri in Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu.
The C25 stage is the most powerful upper stage so far developed by ISRO.
It uses Liquid Oxygen and Liquid Hydrogen propellant combination stored at -253 degrees centigrade.
The development of C25 cryogenic stage will provide ISRO capability to launch 4 ton class satellites in Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO), an altitude where satellites revolve in sync with Earth’s rotation.
So far, the cryogenic engine consisting very complex technology has been developed only by Russia, US, France, China, Japan and India.
This was last test in the series before going for actual GSLV Mark III rocket launch in April 2017 where engine will be put into actual use.
GSLV Mark: Know More
- The GSLV Mark III rocket will be a successor to the GSLV Mark II.
- GSLV Mark 2 was first launched in 2001.
- It can carry a heavier payload than the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle or PSLV.
|
▼ Scientists create graphene from soybean oil [02-20-17]
 Scientists from Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) have made world’s strongest material graphene commercially more viable by using soybean. Scientists from Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) have made world’s strongest material graphene commercially more viable by using soybean.
They have developed a novel “GraphAir technology” which transforms soybean oil, a renewable, natural material into graphene films in a single step.
Previously graphene was produced in a highly-controlled environment with explosive compressed gases that required long hours of operation at high temperatures and extensive vacuum processing.
This production process was costly and was major roadblock in its commercialisation.
The technology grows graphene film in ambient air with a natural precursor, making its production faster and simpler.
Soybean oil breaks down into a range of carbon building units when heat is applied. It makes it essential for the synthesis of graphene films.
Importance of Discovery
This unique technology makes graphene fabrication fast, simple, safe, potentially scalable and integration friendly.
It results in good and transformable graphene properties, comparable to graphene made by conventional methods.
It is expected to reduce cost of graphene production and improve uptake in new applications.
Besides, it can also help to produce graphene from waste oil, leftover from cooking.
All About Graphene
- Graphene is a carbon material that is one atom thick.
- It is the world’s strongest and lightest known material derived from carbon.
- It has high conductivity and excellent electronic, mechanical, thermal and optical properties.
- It is used in many applications ranging from miniaturised electronics to biomedical devices, water filtration and purification, renewable energy, sensors, personalised healthcare and medicine etc.
- It also used to improve battery performance in energy devices, to cheaper solar panels.
|
▼ Dawn Mission: NASA explores Ceres [02-20-17]
 NASA's Dawn mission has found evidence of organic material on Ceres. NASA's Dawn mission has found evidence of organic material on Ceres.
Ceres is a dwarf planet and the largest body in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
Scientists discovered the material in and around a northern-hemisphere crater called Ernutet.
Organic molecules are novel to scientists because they are necessary, though not sufficient components of life on Earth.
The discovery makes it to the growing list of bodies in the solar system where organics have been found.
Organic compounds have been found in certain meteorites. They have also been inferred from telescopic observations of several asteroids.
Ceres shares many commonalities with meteorites rich in water and organics - in particular, a meteorite group referred to as carbonaceous chondrites.
This discovery further strengthens the connection between Ceres, these meteorites and their parent bodies.
This is the first clear detection of organic molecules from orbit on a main belt body.
Data supports the idea that organic materials are native to Ceres.
The carbonates and clays previously identified on Ceres provide evidence for chemical activity in the presence of water and heat.
This raises the chance that the organics were similarly processed in a warm water-rich environment.
The organics discovery makes an addition to Ceres' attributes associated with ingredients and conditions for life in the distant past.
Earlier studies have found hydrated minerals, carbonates, water ice, and ammoniated clays that must have been altered by water.
Salts and sodium carbonate, such as those found in the bright areas of Occator Crater, are also thought to have been carried to the surface by liquid.
This discovery adds to scientific understanding of the possible origins of water and organics on Earth.
The organic materials on Ceres are mainly located in an area covering approximately 1,000 square kilometres.
There are other smaller organic-rich areas several kilometres west and east of the crater.
Organics were also found in a very small area in Inamahari Crater, about 400 kilometres away from Ernutet.
Having completed nearly two years of observations in orbit at Ceres, Dawn is now in a highly elliptical orbit at Ceres, going from an altitude of 7,520 kilometres up to nearly 9,350 kilometres.
It will create a new altitude of around 20,000 kilometres, about the height of GPS satellites above Earth, and to a different orbital plane.
This will put Dawn in a position to study Ceres in a new geometry.
As time advances, Dawn will view Ceres with the sun directly behind the spacecraft, such that Ceres will appear brighter than before, and perhaps reveal more clues about its nature.
Ceres: Find More
- Discovered by: Giuseppe Piazzi
- Discovery date: 1 January 1801
- Named after: Ceres
- Alternative names: A899 OF; 1943 XB
- Minor planet category: Dwarf planet; Asteroid belt
|
▼ Zealandia: The newest continent on earth! [02-20-17]
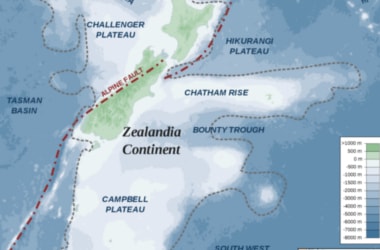 There is an entire, submerged and unrecognised continent that has been hiding until now, according to scientists. There is an entire, submerged and unrecognised continent that has been hiding until now, according to scientists.
New Zealand is sitting on top of the geological entity, most of which sits underneath the South Pacific and so can't be seen.
The researchers explain that Zealandia measures five million sq km which is about two thirds of neighbouring Australia.
The continent - known as Zealandia - is a distinct geological entity and meets all the criteria that are satisfied by the existing seven continents.
It is elevated above the area that surrounds it, has its own distinctive geology, the area that it takes up is well defined.
It also has a crust thicker than the regular ocean floor - just like the seven masses we currently class as continents.
The new continent is 94% under water, according to the new paper.
It is made up of three major landmasses: New Zealand's north and south islands, and New Caledonia to the north.
Scientists said that by classifying it as a continent they would be able to study how they are formed and break up and cohesion of the earth's crust.
Finding data on the continent has been difficult because so much of it is beneath the sea.
Earth's Crust: Know More
- The crust of the Earth is composed of a great variety of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. The crust is underlain by the mantle.
- The upper part of the mantle is composed mostly of peridotite, a rock denser than rocks common in the overlying crust.
- The boundary between the crust and mantle is conventionally placed at the Mohorovicic discontinuity. This is a boundary defined by a contrast in seismic velocity.
- The crust occupies less than 1% of Earth's volume.
|
▼ GA4GH launches ggcINDIA - India's first beacon for genomics data [02-17-17]
 Global Gene Corp and Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) on February 14 launched ggcINDIA, the first ever beacon for Indian genomics data. Global Gene Corp and Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) on February 14 launched ggcINDIA, the first ever beacon for Indian genomics data.
The ggcINDIA Beacon will start to address the lack of shared Indian genomics data.
The ggcINDIA becomes the 69th beacon to join the GA4GH Beacon Network.
A beacon is an online web service that allows researchers to determine whether an institution has particular genomic data in its data set.
The aim of the Indian beacon is to address the gap in shared Indian genomics data.
This helps scientists better understand disease and develop more effective drug delivery systems and therapeutics.
Promise of precision medicine can be realised with usable and sharable genomics data, as per Sumit Jamuar, Chairman & CEO of Global Gene Corp.
The CEO of this Cambridge UK based company is also the creator of the ggcINDIA beacon.
The Indian beacon joins those already on the Wellcome Genome Campus supplied by EMBL-EBI and the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in Hinxton, Cambridgeshire.
Global Gene Corp
- Cambridge-based Global Gene Corp (GCC) is based at the Wellcome Genome Campus.
- It is co-founded by alumni from the Indian Institute of Technology, Harvard and National University of Singapore.
- It was founded with the mission to "democratise genomics".
|
▼ Now, genetic engineering to battle addiction! [02-17-17]
 Mice have been genetically engineered to prevent them from becoming addicted to cocaine. Mice have been genetically engineered to prevent them from becoming addicted to cocaine.
Scientists in Canada created mice that produce higher levels of a protein that normally strengthens the connections between brain cells.
Extra levels of the protein, called cadherin, appeared to make it difficult for a brain cell to receive a signal from others nearby so the pleasurable memory of the cocaine did not remain.
The discovery could help develop new drugs to treat addiction.
For normal learning, scientists must be able to both weaken and strengthen synapses.
That plasticity allows for the pruning of some neural pathways and the formation of others, enabling the brain to adapt and to learn.
Ideally scientists need to find a molecule that blocks formation of a memory of a drug-induced high, while not interfering with the ability to remember important things.
Through genetic engineering, scientists hard-wired in place the synapses in the reward circuits of these mice.
By preventing the synapses from strengthening, they have prevented the mutant mice from 'learning' the memory of cocaine, and thus prevented them from becoming addicted."
|
▼ ISRO launches 104 satellites in 1 mission! [02-16-17]
 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) created history by successfully launching a record 104 satellites in single mission. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) created history by successfully launching a record 104 satellites in single mission.
These satellites were launched on board of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle PSLV-C37, on its 39th mission from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
Of the total 104 satellites, three were Indian and remaining 101 belonged to international customers.
India’s three satellites included earth-mapping Cartosat-2 satellite (main payload) and nano satellites INS-1A and INS-1B.
Of the 101 co-passenger satellites, 96 belong to US and remaining 5 from Israel, Kazakhstan, Netherlands, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates, respectively.
Around 90 small satellites belonged to US-based company Planet Inc.
They are named ‘Doves’ and their constellation will be used to image the earth at low cost.
In this mission, PSLV first launched the Cartosat-2 and then its 103 co-passengers (together weighing about 664 kg) into the polar Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO), about 520 km from the Earth.
This mission beat the previous record held by Russia, which in 2014 had catapulted 37 satellites in a single launch, using a modified inter-continental ballistic missile.
It also broke ISRO’s previous national record set in June 2016, after it had successfully launched 20
The total weight of all the 104 satellites carried on-board PSLV-C37 was 1378 kg.
The total number of Indian satellites launched by PSLV now stands at 46.
Of the 103 co-passenger satellites carried by PSLV-C37, two - ISRO Nano Satellite-1 (INS-1) weighing 8.4 kg and INS-2 weighing 9.7 kg - are technology demonstration satellites from India.
The remaining 101 co-passenger satellites carried were international customer satellites from USA (96), The Netherlands (1), Switzerland (1), Israel (1), Kazakhstan (1) and UAE (1).
This mission involved many technical challenges like realising the launch of a large number of satellites during a single mission within the time frame sought by the customers from abroad.
Besides, ensuring adequate separation between all the 104 satellites during their orbital injection as well as during their subsequent orbital life was yet another challenge associated with this complex mission.
With today’s successful launch, the total number of customer satellites from abroad launched by India’s workhorse launch vehicle PSLV has reached 180.
Cartosat-2 Satellite: Know More
- It was the primary payload of the mission.
- It is similar to the earlier four satellites in Cartosat-2 Series.
- It weighs 714 kg and has a mission life of five years.
- It is earth observation satellite that will provide remote sensing services.
- Images sent by it will be useful for coastal land use and regulation, road network monitoring and creation of land use maps.
- The imagery from the Cartosat-2 series satellite will be useful for: cartographic applications, urban and rural applications, coastal land use and regulation, utility management like road network monitoring, water distribution.
- It will also aid creation of land use maps, change detection to bring out geographical and manmade features and various other Land Information System (LIS) and Geographical Information System (GIS) applications.
- The data sets could be used for urban planning of 500 cities under the Amrut Planning Scheme.
- The government initiative of 100 smart city programme in which these data sets could be used for master plan preparation and detailed geospatial data preparation for rural roads and infrastructure development.
INS-1A and INS-1B Satellites
- They are nano satellites.
- INS-1A was carrying Surface Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function Radiometer.
- INS-1B was carrying Earth Exosphere Lyman Alpha Analyser as payloads.
Launch Vehicle:
- For this mission, ISRO had used XL Variant of PSLV rocket standing 44.4 metres tall and weighing 320 tonnes.
It is most powerful rocket of ISRO and earlier was used in launching ambitious Chandrayaan and Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM).
|
▼ TAMRA: New mining mobile app and portal [02-16-17]
 Union Minister of Mines, Piyush Goyal oversaw the launch the Transparency, Auction Monitoring and Resource Augmentation (TAMRA) Portal and Mobile Application, developed by the Ministry of Mines. Union Minister of Mines, Piyush Goyal oversaw the launch the Transparency, Auction Monitoring and Resource Augmentation (TAMRA) Portal and Mobile Application, developed by the Ministry of Mines.
It was simultaneously launched across 12 mineral rich States.
Goyal also made an important announcement that the Government is planning on bringing amendments to mining rules.
The aim is to bring transparency in award of exploration and mining licences for the 100 identified off-shore mineral blocks soon.
Enhancing Transparency
TAMRA has an objective to enhance transparency and accountability, as a part of the Ease of Doing Business in the Mining sector.
TAMRA is a step to speed up mining activity in India and facilitate all the stakeholders to track the status of the statutory clearances associated with mining blocks for getting mines to reach till operationalisation for the same.
It will be an interactive platform for all the stakeholders to compress the timelines for statutory and other clearances as it would help minimize the gestation period for commencing production.
TAMRA will also send triggers to the concerned authority so that the remedial steps can be taken immediately by those responsible.
The Ministry of Mines will also receive triggers generated by TAMRA, which will facilitate in expediting clearances in case the timelines set against each of the statutory clearances are not met.
Further, the status of each of the clearances will be reflected on the portal.
TAMRA also enables the successful bidder to give suggestions and other inputs for improving the current process of issuing Statutory clearances in the Mining Sector.
This would help to establish a participative and informative network among all stakeholders,
Auction Information
TAMRA covers block-wise, state-wise and mineral-wise information of the mines to be auctioned.
It also monitors various statutory clearances, and highlights the additional resources generated through e-auction.
Further, he also informed that e-auctions have successfully been concluded for 21 mineral blocks put up for auction by various State governments with a total resource base of INR. 93,190 crores.
The total estimated revenue to the State governments through the process of e-auction stands at Rs. 73,359 crores.
Out of this, the cumulative Royalty, District Mineral Fund (DMF) and National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET) contribution works out to be INR. 15,825 crores.
This equals INR. 14,130 crores, INR. 1,413 crores and INR.283 crores, respectively.
|
▼ NETRA: IAF's eye in the sky [02-16-17]
 The Indian Air force (IAF) has formally inducted the first indigenously built Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&C) dubbed as NETRA. The Indian Air force (IAF) has formally inducted the first indigenously built Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&C) dubbed as NETRA.
The AEW&C NETRA has been indigenously developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
It was launched at the 2017 Aero India exhibition held in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
AEW&C are airborne radar systems mounted on a carrier jet for airborne surveillance system.
This is to detect and track aircraft, missiles, ships and vehicles and provide command and control to direct friendly forces.
It consists of active electronically scanned radar, secondary surveillance radar, electronic and communication counter measures, LOS (Line of Sight) and beyond-LOS data link,.
It also has a voice communication system AEW&C NETRA system which is based on Embraer aircraft (Emb-145 platform).
It has self-protection suite and also mid-air refuelling capability to enhance surveillance time.
This system gives 240° coverage of airspace.
DRDO has developed three NETRA systems and its three aircraft will be based at Bhatinda, facing the Western border.
With this India, joins select club of other countries such as United States, Russia and Israel which have developed the AEW&C system.
|
▼ Thubber: Even better than rubber! [02-16-17]
 Scientists have developed novel rubber like material called ‘thubber’ which has high thermal conductivity and elasticity. Scientists have developed novel rubber like material called ‘thubber’ which has high thermal conductivity and elasticity.
Thubber is an electrically insulating composite material that exhibits an unprecedented combination of metal-like thermal conductivity, elasticity similar to soft, biological tissue.
It consists of a soft elastomer with non-toxic, liquid metal micro droplets suspended within it.
This semi-liquid form allows the metal to deform with the surrounding rubber at room temperature.
When it is pre-stretched at room temperature, it stretches up to 6 times its initial length.
During this phase, liquid metal micro-droplets form into elongated pathways through which heat can easily travel through.
Alongside the material is electrically insulating.
In developing wearable computing and soft robotics, industries like athletic wear and sports medicine and in advanced manufacturing, energy, and transportation, thubber can be used.
|
▼ NPPA makes disclosure of cost of stent necessary [02-15-17]
 Tightening the hold over hospitals, nursing homes and clinics performing cardiac procedures using stents, the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) has made it compulsory for such institutions to disclose separately the cost of the stent while billing a patient. Tightening the hold over hospitals, nursing homes and clinics performing cardiac procedures using stents, the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) has made it compulsory for such institutions to disclose separately the cost of the stent while billing a patient.
Medical facilities, including retailers and dealers of stents, will also have to display price list of stents on a part of their premises which is easily accessible to any person wishing to consult the same
Prices of bare metal stents have been capped at INR 7,260, whereas both drugeluting stents (DES) and biodegradable stents will now cost INR 29,600.
The regulator, however, said the new prices will be applicable for a period of one year, unless revised by another gazette notification.
Over 90% of stents implanted in India are DES — metal stents coated with a drug that prevents the arteries from closing again.
Till now, the price of DES in India had ranged anywhere from INR 35,000 to INR 1.95 lakh.
This is considered among the latest stent technology and was priced at around INR 1.80 lakh so far.
|
▼ Tianzhou-1: China's first cargo resupply spacecraft [02-14-17]
 China is planning to launch its first Tianzhou-1 cargo resupply spacecraft through a Long March-7 Y2 carrier rocket in April. China is planning to launch its first Tianzhou-1 cargo resupply spacecraft through a Long March-7 Y2 carrier rocket in April.
This will be a crucial test of key technologies needed for the country's future space station, Xinhua reported on Monday.
The 13-tonne Tianzhou-1 will be launched by a new Long March 7 rocket from Wenchang in April, and dock soon after with the orbiting Tiangong-2 space lab 390 kilometres above the Earth.
This is according to the China Manned Space Agency(CMSA) report.
Tianzhou-1, independently developed by China, can remain in space on its own for as long as three months.
The main objective of the Tianzhou-1 mission is to test and verify on-orbit transfer of liquid propellant to Tiangong-2.
The latter last year hosted two astronauts for China's longest human spaceflight mission so far.
If successful, the spacecraft will be another major step towards China establishing a permanent human presence in space, with the Chinese Space Station(CSS) planned to be completed by 2022.
It is capable of docking with the Tiangong-2 space lab and refuelling it in addition to carrying out experiments and tests.
The Long March-7 Y2 carrier rocket is scheduled to arrive at the launch centre in March, the CMSA added.
|
▼ In a first, solar panels added on Indian warship [02-14-17]
 For the first time in the country, solar panels have been installed on an Indian warship. For the first time in the country, solar panels have been installed on an Indian warship.
The survey class vessel INS Sarvekshak, attached with the southern naval command, has been fitted with 18 sheets of solar panels atop its hangar.
It took about six months to put the entire system in place. We are now using solar energy for lights and a couple of air conditioners.
Captain Rajesh Bargoti is the commanding officer of the ship.
The 300-watt panels generate about 5.4kW power.
Biggest challenge was that marine environments were not suitable for normal solar panels, as saline and humid surroundings would damage it.
Also, the wind speed can affect the panels, which may get uprooted while at sea.
Therefore scientists had to look at flexible panels that had anti-rust properties, were marine compatible, could withstand high wind speeds, perform on flat installations and had very low weight.
There are 10 batteries which are used for storage.
Only solar power for the purpose of lighting during sail.
When anchored the ship uses power supplied by the state electricity board and not diesel.
Ship personnel were noting down meter reading of solar power consumption so as to carry out a power audit and look at using solar power for more devices.
PM Narendra Modi had appreciated the innovation when the project was put on display at the exhibition organised by the Navy headquarters
|
▼ ISRO to launch second mission to moon [02-13-17]
 Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is planning to deploy a rover on the lunar surface in the Chandrayaan-2 mission. Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is planning to deploy a rover on the lunar surface in the Chandrayaan-2 mission.
The Chandrayaan-2, India’s second mission to the Moon, is a totally indigenous mission comprising of an Orbiter, Lander and Rover.
After reaching the 100 km lunar orbit, the Lander housing the Rover will separate from the Orbiter.
After a controlled descent, the Lander will soft land on the lunar surface at a specified site and deploy a Rover.
|
▼ Now, Japanese scientists use drones to pollinate flowers [02-13-17]
 Japanese tinkerers created a tiny, flower-pollinating drone for a world without insects. Japanese tinkerers created a tiny, flower-pollinating drone for a world without insects.
Bee populations are in decline in many parts of the world.
While the reasons bees are in trouble aren’t yet well understood, the problem has some technologists investigating whether drones could fly flower-spreading pollen instead.
The latest effort comes from Japan, where investigators at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science, in Tsukuba, were looking for new uses for sticky substances called ionic liquid gels.
These have unusual physical properties.
Researchers at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology bought $100 drones and affixed patches of horsehair to the bottoms.
They then applied liquid ion gels, which MIT Technology Review says are as sticky and moist as Post-It notes, to the horsehair.
In tests, the drones were able to fly into the plants, grabbing and releasing pollen from the male and female parts of pink and white Japanese lilies.
Project leader Eijiro Miyako claims this was the first time a drone pollinated a flower.
Scientists are also working on genetically modified cyborg dragonflies that can be controlled by humans.
Technology could potentially be used on bees as well.
|
▼ Horse antibodies may effectively treat Ebola [02-13-17]
 In a first, scientists have developed an effective, rapid and economical treatment for the deadly Ebola virus using antibodies from horses. In a first, scientists have developed an effective, rapid and economical treatment for the deadly Ebola virus using antibodies from horses.
The post-exposure treatment made with antibodies from horses could be used in the next Ebola outbreak.
This is a cost-effective treatment that can be used in low-income countries in Africa where equine production facilities are already in operation for producing snake-bite antivenin.
It's the first time that equine antibodies have been shown to work effectively against Ebola infection.
The largest recorded outbreak of Ebola virus occurred primarily in West Africa from 2014 to 2016, infecting 30,000 people and killing more than 11,000, with exported cases in Europe and North America.
The development of monoclonal antibodies were used in the UK to treat infected health workers returning from Africa.
The down side is that monoclonal antibodies require considerable investment for scale-up and manufacture, and are expensive.
Equine antibodies are a considerably cheaper alternative, with manufacturing capacity already in place in Africa.
Antibodies from vaccinated horses provide a low-cost alternative, and are already in use for rabies, botulism and diphtheria.
Scientists have also developed experimental Ebola vaccine made using an Australian virus called Kunjin, that might also help in the fight against the deadly Ebola virus.
|
▼ BHIM launched on iOS platform [02-13-17]
 BHIM, which the government has developed for fast and secure cashless transactions, was on 11th Feb 2017 launched on the iOS platform. BHIM, which the government has developed for fast and secure cashless transactions, was on 11th Feb 2017 launched on the iOS platform.
“The much awaited #BHIM for iOS is now available on the AppStore. Apple users, download #BHIM now! #ItPaystoBHIM," Niti Aayog indicated in a tweet.
The Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) was available on Android platform.
On December 30, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched the app for fast and secure cashless transactions using mobile phones.
BHIM is a platform designed to make payment through UPI and USSD modes simpler.
The number of downloads for BHIM app has crossed 1 crore mark.
The BHIM app downloads which have shot up in a matter of a few days "shows how India is changing" with regard to adoption of digital payments and cashless transaction.
Digital payment channels like mobile wallets, USSD and RuPay have seen massive uptake and rise in transactions post demonetisation.
According to government data, the number of transactions on USSD (mobile short code message used mainly for banking services on feature phone) saw a massive 5,135 per cent jump.
The increase was from 97 such deals a day on November 8 to 5,078 on December 25.
UPI transactions - which allows users to transfer funds from one bank account to another using a smartphone - grew 1,342 per cent.
This is from 3,721 such transactions a day on November 8 to 53,648 on December 25.
BHIM: Know More
- Developer: National Payments Corporation of India
- Initial release: 30 December 2016
- Platform: Google Play, App Store
- Available in: English, Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Gujarati
- Type: Payment
- Website: NPCI Portal
|
▼ Rufous-tailed Rock Thrush - Nepal's newest discovery [02-13-17]
 A new species of birds has been discovered in the high mountainous region of Nepal. A new species of birds has been discovered in the high mountainous region of Nepal.
This is bringing the total number of avian species in the Himalayan country to 866.
A Rufous-tailed Rock Thrush (Monticola saxitilis), considered an autumn passage migrant bird species in Pakistan and India, was photographed by an expedition near the Shey monastery within the Shey-Phoksundo National Park.
Researchers from an NGO Friends of Nature (FoN) Nepal spotted the bird while studying Himalayan wolf, wild yak and snow leopard last year.
The identification of the bird reported by the team was confirmed by the bird experts Carol Inskipp and Hem Sagar Baral.
The Department of National Parks and Wildlife Conservation (DNPWC) and Bird Conservation Nepal authorised the presence of a new bird species in the country.
Rufous-tailed Rock Thrush is considered an autumn passage migrant bird species in Pakistan and India.
The sighting location was very remote and rarely visited by ornithologists.
About the Rufous-tailed Rock Thrush
- The common rock thrush, formerly rufous-tailed rock thrush or rock thrush.
- This bird is belonging to the family Muscicapidae.
- It was formerly placed in the family Turdidae.
- Scientific name: Monticola saxatilis
- Higher classification: Rock thrush
- Rank: Species
|
▼ India takes a step towards Two tier BMD system [02-13-17]
 India took a big step towards an operational two-tier ballistic missile defence (BMD) system by testing a high-altitude interceptor missile to destroy an incoming ballistic missile over the Bay of Bengal on 11th Feb 2017. India took a big step towards an operational two-tier ballistic missile defence (BMD) system by testing a high-altitude interceptor missile to destroy an incoming ballistic missile over the Bay of Bengal on 11th Feb 2017.
This missile can destroy an enemy missile high in the sky. Only four to five countries in the world have done this.
The Defence Research and Development Organisation was itself gung-ho about its long-delayed BMD system, claiming it would now be possible to deploy the two-layered missile shield to protect a city or strategic installation in two years.
But it had earlier also promised that New Delhi would get the missile shield, capable of tackling hostile missiles with a 2,000-km strike range, by 2014 at the latest.
Scientists, however, say they are confident of achieving the target this time.
The "exo-atmospheric" interceptor missile tested on 11th Feb 2017, also called the PDV (Prithvi defence vehicle), after all, directly hit the target missile at an altitude of 97 km.
The test began at 7.45 am with the two-stage target missile, replicating an enemy ballistic missile, being launched from a ship in the Bay of Bengal.
In the fully-automated operation, with long-range radars continuously tracking the target and feeding data about its trajectory to the mission computers, the interceptor missile was then fired from the Abdul Kalam Island (Wheeler Island) off Odisha coast around 200-km away.
India has crossed an important milestone in building its overall capability towards enhanced security against incoming ballistic missile threats.
It has entered an exclusive club of four nations (US, Russia, China and Israel) by developing capabilities to secure its skies and cities against hostile threats.
DRDO's experimental two-tier system is designed to track and destroy ballistic missiles both inside (endo) and outside (exo) the earth's atmosphere.
The third layer, in turn, is planned to tackle low-flying cruise missiles, artillery projectiles and rockets in the line with the overall aim to achieve near 100% kill or interception probability'.
Phase-I of the BMD system, with interceptors flying at 4.5 Mach high-supersonic speeds to intercept enemy missiles, is meant to tackle hostile missiles with a 2,000-km strike range.
Phase-II will be geared for taking on 5,000-km range missiles, with interceptors at hypersonic speeds of 6-7 Mach.
BMD Systems: Know More
- BMD systems are highly complex to develop and deploy.
- They require an overlapping network of early-warning and tracking sensors.
- They also need reliable command and control posts, land and sea-based batteries of advanced interceptor missiles.
- BMD systems also cannot ensure 100% destruction of all incoming hostile missiles.
|
▼ Scientists discover cave housing Dead Sea Scrolls [02-10-17]
 Archaeologists have uncovered a new cave that once housed Dead Sea Scrolls. Archaeologists have uncovered a new cave that once housed Dead Sea Scrolls.
This is a discovery described as one of the “most important” in 60 years.
The Hebrew University in Jerusalem said the scrolls were missing from the cave.
The Dead Sea Scrolls include the oldest known manuscripts of the Hebrew Bible.
These date from the 3rd century BCE to the 1st century CE.
About 900 scrolls were discovered between 1947 and 1956 in the Qumran caves above the Dead Sea.
The parchment and papyrus scrolls contain Hebrew, Greek and Aramaic writing, and include several of the earliest-known texts from the Bible.
This is including the oldest surviving copy of the Ten Commandments.
This discovery of a 12th cave could revolutionise the information and herald most important” discoveries since 1956.
The cave discovered west of Qumran in the occupied West Bank contained no manuscripts, but there is ample evidence of their earlier presence.
This includes fragments of pottery in which they were placed and the leather straps.
Many of the caves containing the manuscripts were looted in the 1950s.
|
▼ This black hole weighs as much as 2,200 suns! [02-10-17]
 An important cosmic missing link has been found: a middle sized black hole. An important cosmic missing link has been found: a middle sized black hole.
Till now, scientists had found either small black holes weighing a few Suns or supermassive black holes weighing millions or billions of Suns, like the one at the centre of our galaxy, the Milky Way.
But in an ancient cluster of stars some 13,000 light years away from Earth, scientists discovered an intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH) weighing 2,200 Suns.
It was hiding at the centre of the globular star cluster 47 Tucanae.
Such holes serve as missing link between stellar-mass and supermassive black holes. They may be the primordial seeds that grew into the monsters seen in the centres of galaxies.
47 Tucanae had been examined for a central black hole before without success.
In most cases, a black hole is found by looking for X-rays coming from a hot disk of material swirling around it.
This method only works if the black hole is actively feeding on nearby gas.
The centre of 47 Tucanae is gas-free, effectively starving any black hole that might lurk there.
A black hole also betrays its presence by its influence on nearby stars causing them to speed up.
But the crowded centre of 47 Tucanae makes it impossible to watch the motions of individual stars.
Scientists studying 47 Tucanae found that heavy stars nearer the centre were getting speeded up and flung away as if a cosmic "spoon" was stirring the pot.
This was measured by the astronomers and compared with computer simulations, leading them to conclude that there was some very heavy body at the center causing this gravitational stirring.
Pulsars were also found at greater distances from the cluster's centre than would be expected if no black hole existed.
Combined, this evidence suggests the presence of an IMBH of about 2,200 solar masses within 47 Tucanae.
47 Tucanae: Know More
- 47 Tucanae is a 12-billion-year-old star cluster located in the southern constellation of Tucana the Toucan.
- It contains thousands of stars in a ball only about 120 light-years in diameter.
- It also holds about two dozen pulsars that were important targets of this investigation.
|
▼ A battery that would run on stomach acid [02-9-17]
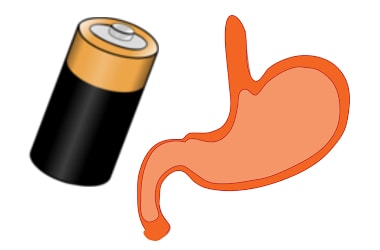 MIT researchers have developed a small battery that runs on stomach acids and is capable of powering e-pills to monitor patient health. MIT researchers have developed a small battery that runs on stomach acids and is capable of powering e-pills to monitor patient health.
The small system can generate enough power to run small sensors or drug delivery devices that can reside in the gastrointestinal tract for long periods of time.
For this battery, researchers used idea of very simple type of voltaic cell, lemon battery that produces electric current between the two electrodes stuck in a lemon due to its citric acid.
To replicate it, the researchers attached zinc and copper electrodes to the surface of their ingestible sensor.
The zinc emits ions into the acid in the stomach to power the voltaic circuit.
It can generate enough energy to power a commercial temperature sensor and a 900-megahertz transmitter to wirelessly transmit the data to a base station located 2 metres away, with a signal sent every 12 seconds.
The current prototype of the device is a cylinder about 12 millimetres in diameter and 40 millimetres in length.
Researchers are anticipating to make the capsule about one-third that size.
It offers a safer and lower-cost alternative to the traditional batteries used to power such devices.
It can also help in manufacturing new generation of electronic ingestible pills.
This could enable novel ways of monitoring patient health and treating disease.
|
▼ One of its kind white dwarf pulsar! [02-9-17]
 Astronomers have located an elusive white dwarf pulsar. This is the first of its kind to be discovered in the universe. It is housed in an exotic binary star system 380 light years away from Earth. Astronomers have located an elusive white dwarf pulsar. This is the first of its kind to be discovered in the universe. It is housed in an exotic binary star system 380 light years away from Earth.
Researchers identified the star AR Scorpii (AR Sco) as the first white dwarf version of a pulsar.
Fresh data shows that AR Sco's light is highly polarised, showing that the magnetic field controls the emission of the entire system.
This is a dead-ringer for similar behaviour seen from the more traditional neutron star pulsars.
The white dwarf pulsar has eluded astronomers for over five decades.
AR Sco contains a rapidly spinning, burnt-out stellar remnant called a white dwarf, which lashes its neighbour- a red dwarf.
It does so through powerful beams of electrical particles and radiation, causing the entire system to brighten and fade dramatically twice every few minutes.
The lash of energy from AR Sco is a focused 'beam', emitting concentrated radiation in a single direction much like a particle accelerator- something which is totally unique in the known universe.
AR Sco lies in the constellation Scorpius, 380 light years from Earth, a close neighbour in astronomical terms.
The white dwarf in AR Sco is the size of Earth but 200,000 times more massive. It is in a 3.6 hour orbit with a cool star one-third the mass of the Sun, as per the study.
What is a Pulsar?
- They are what is known as the “lighthouses” of the universe.
- These are rotating neutron stars that emit a focused beam of electromagnetic radiation that is only visible if you’re standing in it’s path.
- Referred to as pulsars, these stellar relics get their name because of the way their emissions appear to be “pulsating” out into space.
- Pulsars are types of neutron stars which are the dead relics of massive stars.
- They are highly magnetized, and rotating at enormous speeds.
- Astronomers detect them by the radio pulses they emit at regular intervals.
|
▼ ISRO indigenously develops TTCP [02-9-17]
 ISRO has indigenously developed Telemetry and Telecommand Processor. Its production will commence with the help of the Indian industry. ISRO has indigenously developed Telemetry and Telecommand Processor. Its production will commence with the help of the Indian industry.
Processor's indigenous development was taken as part of Make in India, replacing expensive imported equipment.
TTCP will be used in Integrated Spacecraft Testing of Low Earth Orbit, Geostationary Orbit and Interplanetary Spacecraft, ISRO said.
This system is configurable to meet uplink and downlink requirements of both CCSDS (Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems) and ISRO standards.
Number of multiple clients can remotely access this system for data and monitoring.
Spacecraft Checkout Group of ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC) is responsible for integrated spacecraft testing to ensure the flight worthiness of the spacecraft built at ISAC.
Pointing out that during the testing, ground systems will communicate to spacecraft via the same uplink and downlink signals.
This is because as in space, the spacecraft typically use ISRO formats for telemetry and telecommand (downlink and uplink), for which indigenous equipment are being used.
However, the interplanetary spacecraft use an international standard known as CCSDS, and presently equipment are being imported for telemetry reception and telecommand transmission requirements.
This indigenously developed Processor was successfully deployed for the first time in checkout of GSAT-19, which is scheduled to be launched shortly.
All About GSAT-19
- GSAT-19E is an Indian communications satellite scheduled by the Indian Space Research Organisation for launch aboard a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III on 20 January 2017.
- Launch date: December 2016
- Launch mass: 3,200 kg
- Launch mass: 3,200 kg
- Bus: I-3K
- Mission type: Communications satellite
- Manufacturers: Indian Space Research Organisation Satellite Centre, Space Applications Centre
|
▼ First stable helium-sodium compound created in lab! [02-8-17]
 Helium is the second most abundant element in the Universe Helium is the second most abundant element in the Universe
It belongs to a six-member group of elements called the noble gases.
These are so-called because of an apparent 'aloofness' that prevents them from easily forming compounds with other elements.
Since earning their 'noble' reputation, some of these gases have shown signs of reactiveness under extreme conditions.
One can actually split the noble gases up into two groups, with krypton, xenon, and radon considered to be relatively reactive, and argon, neon, and helium considered to be very unreactive.
Researchers have found ways to pair up helium with other elements in the past, but until now, the result has always been less than concrete.
One of the most common examples of helium interacting with other elements refers to van der Waals forces - attractive or repulsive forces that don't require conventional covalent or ionic bonds to form.
It's known that very weak van der Waals forces exist between helium and other atom.
At extremely low temperatures, helium can form van der Waals molecules - very weakly bound clusters of atoms or molecules - but they cannot be sustained for long.
Helium's staunch stability is due to its closed-shell electronic configuration - its outer shell is complete, which means there's no room for it to bond with other atoms by sharing electrons.
Being one of the most abundant elements in the Universe, responsible for forming stars and gas giant planets, helium could play by very different rules out in space and deep within our planet.
The researchers have just found the first evidence yet of that weird behaviour.
The researchers used a 'crystal structure-predicting' computer model to predict that under extreme pressures, a stable helium-sodium compound could form.
They then physically created the never-before-seen compound, Na2He, in a diamond anvil cell experiment.
This allowed them to subject helium and sodium atoms to pressures of around 1.1 million times Earth's atmospheric pressure.
"These findings were so unexpected, scientists and their colleagues struggled for more than two years to convince science reviewers and editors to publish their results.
Based on this, sodium will easily bond with helium gas to form a stable Na2He compound under pressures up to 10 million times higher than the level they achieved it at.
The compound appears to form without any chemical bonds to hold it together.
Helium atoms do not actually form any chemical bonds, yet their presence fundamentally changes chemical interactions between sodium atoms, forces electrons to localise inside cubic voids of the structure, and makes this material insulating.
Here's the crystal structure of Na2He - a solid formation of alternating sodium and helium atoms, with electrons shared in the voids between them.
Chemists have made a number of these 'rule-breaking' discoveries recently, with separate teams creating the world's first sample of metallic hydrogen, and a carbon molecule with six - not four - bonds last month.
This helium compound is a breakthrough.
Helium: Know More
- Symbol: He
- Atomic mass: 4.002602 u ± 0.000002 u
- Atomic number: 2
- Electron configuration: 1s2
- Discovered: 1868
- Melting point: -272.2°C
- Discoverers: Pierre Janssen, Norman Lockyer
|
▼ Measles rubella vaccine campaign added to flagship Universal Immunisation Programme [02-6-17]
 Adding a new vaccine to its flagship Universal Immunisation Programme, the Union health ministry launched measles rubella (MR) vaccination campaign on 5th Feb 2017. Adding a new vaccine to its flagship Universal Immunisation Programme, the Union health ministry launched measles rubella (MR) vaccination campaign on 5th Feb 2017.
The campaign will soon be followed by roll out of the vaccine in routine immunisation, an official said.
The single vaccine will come in place of the currently given two doses of measles vaccine at 9-12 months and 16-24 months of age.
The new single shot vaccine will be provided to all children aged between 9 months and less than 15 years irrespective of their previous measles or rubella vaccination status or measles or rubella disease status.
MR vaccine will be provided free-of-cost across states at schools as well as health facilities and outreach session sites.
The awareness campaign targets around 41 crore children across the country, the largest ever in any campaign.
In the first phase, the campaign will cover five states — Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry, Goa and Lakshadweep.
It will be covering nearly 3.6 crore children.
Partners for the programme include states, NGOs and development partners such as WHO, Unnicef, Gates Foundation, Lions Club, IPA, IMA.
|
▼ World's tiniest hammer: MicroHammer [02-6-17]
 Researchers have created the world's tiniest hammer to measure how force affects brain cells. Researchers have created the world's tiniest hammer to measure how force affects brain cells.
This will pave the way for better cure of traumatic brain injuries and Alzheimer's.
University of California researchers have built a tiny machine called microHammer.
Far from being isolated units of life, cells stem cells in particular take cues from their environment.
This, for example, direct them to differentiate into one type of cell or another, or to start healing processes.
However, a major limitation to understanding the reactions of individual cells to forces has been the inability to reliably apply impact or pressure to them.
MicroHammer, a cellular-scale machine built to tap, strike, squeeze and poke individual neural progenitors elicits responses that will then be studied and recorded to add to a body of knowledge that can help unlock the mysteries of the brain.
|
▼ China successfully tests DF-5C missile with 10 nuclear warheads [02-6-17]
 China has tested a new version of a missile that can carry up to 10 nuclear warheads. China has tested a new version of a missile that can carry up to 10 nuclear warheads.
This is signalling a major shift in its nuclear capability as Beijing gears up for a possible military showdown with the US under Trump Presidency.
The flight test of the DF-5C missile was carried out last month using 10 multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles, or MIRVs.
The test of the inert warheads was monitored closely by U.S. intelligence agencies.
The DF-5 is a two-stage, liquid-fueled missile with a range of around 8,000 miles.
The missile was fired from the Taiyuan Space Launch Center in central China and flew to an impact range in the western Chinese desert.
The test of a missile with 10 warheads is significant because it indicates the secretive Chinese military is increasing the number of warheads in its arsenal, the website reported.
Estimates of China's nuclear arsenal for decades put the number of strategic warheads at the relatively low level of around 250 warheads.
U.S. intelligence agencies in February reported that China had begun adding warheads to older DF-5 missiles, in a move that has raised concerns for strategic war planners.
Uploading Chinese missiles from single or triple warhead configurations to up to 10 warheads means the number of warheads stockpiled is orders of magnitude larger than the 250 estimate.
Currently, U.S. nuclear forces - land-based and sea-based nuclear missiles and bombers - have been configured to deter Russia's growing nuclear forces and the smaller Chinese nuclear force.
Under the 2010 U.S.-Russian arms treaty, the United States is slated to reduce its nuclear arsenal to 1,550 deployed warheads.
A boost in the Chinese nuclear arsenal to 800 or 1,000 warheads likely would prompt the Pentagon to increase the U.S. nuclear warhead arsenal by taking weapons out of storage.
|
▼ NASA spots farthest galaxies fuelled by massive black holes [02-6-17]
 NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has identified the farthest gamma-ray blazars. NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has identified the farthest gamma-ray blazars.
This is a type of galaxy whose intense emissions are powered by supersized black holes.
Light from the most distant object began its journey to us when the universe was 1.4 billion years old, or nearly 10 percent of its present age.
Experts say they could shed fresh light on how black holes form.
What is a Black Hole?
- A black hole is a region of spacetime exhibiting strong gravitational effects.
- Nothing - not even particles and electromagnetic radiation such as light - can escape from inside it.
- The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform space time to form a black hole.
|
▼ Madrid park becomes home to first pedestrian 3D bridge [02-6-17]
 A Madrid park made history with the installation of the first ever pedestrian bridge created from a 3D printer. A Madrid park made history with the installation of the first ever pedestrian bridge created from a 3D printer.
The pioneering bridge was created by a team from the Institute of Advanced Architecture of Catalonia, a Barcelona based research and education center that worked with a contingent of architects, mechanical and structural engineers, and municipal representatives to bring the design to life.
The 40ft bridge spans a stretch of water in the Castilla-La Mancha park in Alcobendas, north of the Spanish capital.
It has beaten a 3D printing construction project, a steel bridge coming up over a canal in Amsterdam.
Meanwhile, the Madrid bridge is made up of eight parts, each one comprising layers of fused concrete powder micro-reinforced with thermoplastic polypropylene.
The 3D printed bridge, which reflects the complexities of nature's forms, was developed through parametric design, which allows to optimize the distribution of materials and minimize the amount of waste by recycling the raw material during manufacture.
It's a milestone for the construction sector at international level, since, to date, this technology has not been applied in the field of civil engineering.
|
▼ Scientists find lost continent under Indian Ocean island of Mauritius [02-3-17]
 Scientists confirm the existence of a lost continent under Indian Ocean's Mauritius island. Scientists confirm the existence of a lost continent under Indian Ocean's Mauritius island.
It is left over by the break-up of the super-continent Gondwana, which started about 200 million years ago.
The discovery was based on study of Zircon, a mineral found in rocks spewed up by lava during volcanic eruptions which is too old to belong to Mauritius.
The lost continent is just a small piece of island that probably broke of when Africa, India, Australia and Antarctica split up and formed the Indian Ocean.
The scientists found zircons on the island of Mauritius that are 3 billion years old.
These remnants are too ancient to belong to Mauritius as it has no rock older than 9 million years old.
The piece of crust of lost continent was subsequently covered by young lava during volcanic eruptions.
There are many pieces of various sizes of undiscovered continent which are collectively called as Mauritius.
Zircon: Know More
- Zircons are minerals that occur mainly in granite from the continents.
- They contain trace amounts of uranium, thorium and lead.
- They can survive geological processes.
- They contain a rich record and can be dated extremely accurately.
|
▼ Chinese scientists develop bovine resistant live cows [02-3-17]
 Chinese scientists from Northwest A&F University have produced world’s first live cows. Chinese scientists from Northwest A&F University have produced world’s first live cows.
This has increased resistance to bovine tuberculosis (TB).
This development shows that genetic modification technology can be better suited to producing transgenic livestock with purposefully manipulated genetic.
Researchers had used a modified version of the CRISPR gene-editing technology called CRISPR/Cas9n.
This is to insert a new TB resistance gene NRAMP1 into the genome of bovine foetal fibroblasts, cell derived from female dairy cows.
These cells were then used as donor cells in a process called somatic cell nuclear transfer.
In it, nucleus of a donor cell carrying the new gene was inserted into an egg cell, known as an ovum, from a female cow.
These ovum were then nurtured in the lab into embryos and transferred into mother cows for a normal pregnancy cycle.
During this cycle, cows were produced with no off target effects on the animals’ genetics - a common problem when creating transgenic animals using CRISPR.
This scientific process revealed that NRAMP1 had successfully integrated into the genetic code at the targeted region in all of the calves.
When it was exposed to Mycobacterium bovis (M. bovis), bacterium that causes bovine TB, transgenic animals showed increased resistance to M. bovis.
Further in laboratory tests, the white blood cells taken from the calves also showed much resistance to M. bovis exposure.
CRISPR-Cas9: Know More
- CRISPR is the short form of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats.
- It allows scientists to selectively edit genome parts and replace them with new DNA stretches.
- Cas9 is an enzyme that can edit DNA, allowing the alteration of genetic patterns by genome modification.
- CRISPR is a collection of DNA sequences that direct Cas9 where to cut and paste.
- CRISPR-Cas9 technology has the potential to revolutionise the treatment of blood diseases, tumours and other genetic diseases.
|
▼ This sea animal is earliest known ancestor of humans! [02-2-17]
 Researchers have discovered microscopic sea animal Saccorhytus. Researchers have discovered microscopic sea animal Saccorhytus.
This is the earliest known ancestor of humans along with a vast range of other species.
The exquisitely well preserved fossilised traces of this 540-million-year-old creature were discovered by researchers.
This balloon-like sea is the earliest known step on the evolutionary path that led to fish and eventually to humans.
Saccorhytus is the most primitive example of deuterostomes.
This is a category of animals which are common ancestors of a broad range of species, including vertebrates (backboned animals).
It was about a millimetre and its body was symmetrical.
This is a characteristic inherited by many of its evolutionary descendants, including humans.
It was also covered with a thin, relatively flexible skin and muscles which concludes that it moved by contracting its muscles and got around by wriggling.
It is estimated to have lived between grains of sand on the sea bed.
It had large mouth, relative to the rest of its body indicating that it probably ate by engulfing food particles, or even other creatures.
Its body also had conical structures which might have allowed the water swallowed by it to escape. It also indicates these conical structures might have been an early version of gills.
|
▼ Bangladesh's first Tree Man Disease case uncovered [02-2-17]
 Doctors in Bangladesh will form a medical board to assess a 10-year-old girl with bark-like warts growing out of her face. Doctors in Bangladesh will form a medical board to assess a 10-year-old girl with bark-like warts growing out of her face.
She is believed to be suffering from tree-man syndrome, a rare genetic hereditary skin disorder.
A six-member medical board will be formed to assess Shahana Khatun's illness, Dr Samanta Lal of Dhaka Medical College Hospital..
Her treatment will be free of cost, according to a media report.
Shahana Khatun's father Shahjahan Mia, a farmer became concerned when a growth previously thought to be prickly heat rashes started to spread and grow on his daughters face,
Previously, Abul Bajandar, 26, also known as "tree man" has undergone at least 18 operations at the same hospital where Shahana is receiving treatment.
Tree-man disease is a rare skin disorder, which covers limbs with warts, making them look like tree branches.
A Romanian man was first diagnosed with the disease in March 2007. Another case was reported in Indonesia in November the same year in a 35-year-old fisherman.
The last reported case also occurred in Indonesia in 2009.
About Tree Man Disease
- Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV, also called Lewandowsky–Lutz dysplasia)
- This is colloquially known as tree man illness.
- It is is an extremely rare autosomal recessive genetic hereditary skin disorder associated with a high risk of carcinoma of the skin.
- It is characterized by abnormal susceptibility to human papillomaviruses (HPVs) of the skin.
- This will result in the growth of scaly macules and papules, particularly on the hands and feet.
- The condition usually has an onset of between the ages of one and 20, but can occasionally present in middle age.
- Discovered by: Felix Lewandowsky and Wilhelm Lutz (de).
|